Localized Provoked Vulvodynia-An Ignored Vulvar Pain Syndrome
- PMID: 34222047
- PMCID: PMC8248677
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.678961
Localized Provoked Vulvodynia-An Ignored Vulvar Pain Syndrome
Abstract
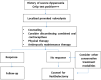
Localized provoked vulvodynia (LPV) causes dyspareunia among reproductive aged women. We review the pathogenesis of LPV and suggest that LPV is an inflammatory pain syndrome of the vestibular mucosa triggered by microbial antigens in a susceptible host. Tissue inflammation and hyperinnervation are characteristic findings which explain symptoms and clinical signs. Education of health care providers of LPV is important since this condition is common, often unrecognized, and patients often become frustrated users of health care. Research is needed on the antigen triggers of the syndrome. Randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate treatment modalities.
Keywords: localized provoked vulvodynia; vulvar pain; vulvar pain syndrome; vulvar vestibulitis syndrome; vulvodynia.
Copyright © 2021 Paavonen and Eschenbach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice. American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) (2016). Committee Opinion No 673: Persistent Vulvar Pain. Obstet. Gynecol. 128 (3), e78–e84. - PubMed
-
- Bohm-Starke N., Johannesson U., Hilliges M., Rylander E., Torebjörk E. (2004). Decreased Mechanical Pain Threshold in the Vestibular Mucosa of Women Using Oral Contraceptives: A Contributing Factor in Vulvar Vestibulitis? J. Reprod. Med. 49, 888–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

