Nephroprotective effect of Vanillic acid in STZ-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 34222078
- PMCID: PMC8212202
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00782-7
Nephroprotective effect of Vanillic acid in STZ-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the protective effect of vanillic acid (VA) in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic nephropathy (DN) in rats.
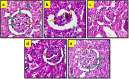
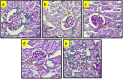
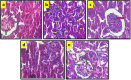
Methods: Experimental diabetes mellitus in rats was induced by intraperitoneally administration of single dose of STZ (55 mg/kg). The animals were divided into 5 groups viz., normal control, diabetic control, glimepiride (0.5 mg/kg, orally) and VA treatment (50 and 100 mg/kg, orally) groups. The treatment was started after the confirmation of hyperglycemia (> 250 mg/dl) and continued for 6 weeks. Serum glucose level, and body weight were measured weekly. At the end of study, HbA1c in whole blood, insulin, lipid profile, urea, creatinine and albumin in serum. Creatinine and albumin were measured in urine along with creatinine clearance. In addition, kidney weight and histopathology were assessed.
Results: Treatment with VA markedly attenuated STZ-induced body weight loss and hyperglycemia, along with improved lipid profile and HbA1c, without significant alteration of serum insulin levels. It also decreased urea, creatinine and increased albumin in serum. Moreover, VA, significantly reduced urine volume, urinary albumin along with marked improvement in creatinine clearance. Further, the VA treatment significantly reverse the raised levels of oxidative stress markers, pro-inflammatory and fibrotic markers viz. TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β1 and NFκB activity in kidney tissue. These effects are associated with amelioration of histopathological alterations compared to diabetic control rats. While glimepiride produced similar antihyperglycemic effect but the effect on albuminuria, oxidative stress markers and cytokine levels were less significant as compared to VA (100 mg/kg).
Conclusions: In conclusion, VA exhibited nephroprotective effect through amelioration of kidney dysfunction and damage in diabetic rats. The observed nephroprotective effect of VA may be ascribed to inhibition of hyperglycemia induced oxido-inflammatory stress and necroptosis of renal tissue possibly due to its antihyperglycemic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Antioxidants; Gimepiride; Insulin; Necroptosis; Vanillic acid.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of vanillic acid against diabetes and diabetic nephropathy by attenuating oxidative stress and upregulation of NF-κB, TNF-α and COX-2 proteins in rats.Phytother Res. 2022 Mar;36(3):1338-1352. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7392. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35088468
-
Diltiazem attenuates oxidative stress in diabetic rats.Ren Fail. 2005;27(3):335-44. Ren Fail. 2005. PMID: 15957552
-
Nephroprotective effect of Combretum micranthum G. Don in nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy in rats: In-vivo and in-silico experiments.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 28;261:113133. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113133. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32673708
-
The anti-inflammation effect of Moutan Cortex on advanced glycation end products-induced rat mesangial cells dysfunction and High-glucose-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):591-600. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.015. Epub 2013 Nov 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24269777
-
Antidiabetic and Nephroprotective Effects of Polysaccharide Extract from the Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa in High Fructose-Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Nephropathy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 May 12;14:2121-2131. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S302748. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34012278 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metabolite Profiling and Nephroprotective Potential of the Zea mays L. Silk Extract against Diclofenac-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Wistar Rats.ACS Omega. 2022 Oct 7;7(41):36519-36534. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04396. eCollection 2022 Oct 18. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36278090 Free PMC article.
-
Selected Seeds as Sources of Bioactive Compounds with Diverse Biological Activities.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):187. doi: 10.3390/nu15010187. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vanillic acid as a promising intervention for metabolic syndrome: Preclinical studies.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(2):141-150. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.81709.17680. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39850111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo and computational investigation of butin against alloxan-induced diabetes via biochemical, histopathological, and molecular interactions.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 4;14(1):20633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71577-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39232184 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of vanillic acid on letrozole-induced polycystic ovarian syndrome: A comprehensive study in female wistar rats.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Feb;32(2):101953. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101953. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38288132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF. Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. 2019. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
-
- Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:137–88. - PubMed
-
- Varghese RT, Jialal I. Diabetic Nephropathy. :Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing LLC. 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534200/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

