Heat Shock Proteins: Potential Modulators and Candidate Biomarkers of Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 34222357
- PMCID: PMC8241919
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.633013
Heat Shock Proteins: Potential Modulators and Candidate Biomarkers of Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
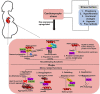
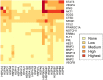
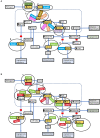
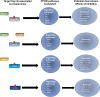
Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) is a potentially life-threatening condition in which heart failure and systolic dysfunction occur late in pregnancy or within months following delivery. To date, no reliable biomarkers or therapeutic interventions for the condition exist, thus necessitating an urgent need for identification of novel PPCM drug targets and candidate biomarkers. Leads for novel treatments and biomarkers are therefore being investigated worldwide. Pregnancy is generally accompanied by dramatic hemodynamic changes, including a reduced afterload and a 50% increase in cardiac output. These increased cardiac stresses during pregnancy potentially impair protein folding processes within the cardiac tissue. The accumulation of misfolded proteins results in increased toxicity and cardiac insults that trigger heart failure. Under stress conditions, molecular chaperones such as heat shock proteins (Hsps) play crucial roles in maintaining cellular proteostasis. Here, we critically assess the potential role of Hsps in PPCM. We further predict specific associations between the Hsp types Hsp70, Hsp90 and small Hsps with several proteins implicated in PPCM pathophysiology. Furthermore, we explore the possibility of select Hsps as novel candidate PPCM biomarkers and drug targets. A better understanding of how these Hsps modulate PPCM pathogenesis holds promise in improving treatment, prognosis and management of the condition, and possibly other forms of acute heart failure.
Keywords: biomarkers; cardiomyopathy; drug targets; heat shock protein; pregnancy; stress.
Copyright © 2021 Chakafana, Spracklen, Kamuli, Zininga, Shonhai, Ntusi and Sliwa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetics of Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: Current Knowledge, Future Directions and Clinical Implications.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 15;12(1):103. doi: 10.3390/genes12010103. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33467574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Mystery of Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: A Traditional Review.Cureus. 2020 Oct 4;12(10):e10790. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10790. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33042652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripartum cardiomyopathy: basic mechanisms and hope for new therapies.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Mar 1;116(3):520-531. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz252. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31605117 Review.
-
EURObservational Research Programme: a worldwide registry on peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) in conjunction with the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on PPCM.Eur J Heart Fail. 2014 May;16(5):583-91. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.68. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014. PMID: 24591060
-
Heat shock proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential.Int J Cancer. 2016 Apr 15;138(8):1824-34. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29723. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26853533 Review.
Cited by
-
Precision medicine in peripartum cardiomyopathy: advancing diagnosis and management through genomic and phenotypic integration.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jul 1;86(8):4664-4667. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002329. eCollection 2024 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39118717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy-What We Know and What Is Still to Be Found.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 12;14(1):103. doi: 10.3390/biom14010103. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38254703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteotoxic stress response in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Emerging role of heat shock factor 1.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 3;10:1155444. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1155444. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37077734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning enhances aerobic performance by accelerating regional oxygenation and improving cardiac function during acute hypobaric hypoxia exposure.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 9;13:950086. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.950086. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36160840 Free PMC article.
-
Peripartum cardiomyopathy: a comprehensive and contemporary review.Heart Fail Rev. 2024 Nov;29(6):1261-1278. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10435-5. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Heart Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 39348083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauersachs J, Konig T, van der Meer P, Petrie MC, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Mbakwem A, et al. . Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of peripartum cardiomyopathy: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology Study Group on peripartum cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail. (2019) 21:827–43. 10.1002/ejhf.1493 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

