The Predictive Value of Right Ventricular Longitudinal Strain in Pulmonary Hypertension, Heart Failure, and Valvular Diseases
- PMID: 34222387
- PMCID: PMC8247437
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.698158
The Predictive Value of Right Ventricular Longitudinal Strain in Pulmonary Hypertension, Heart Failure, and Valvular Diseases
Abstract
Right ventricular (RV) systolic function has an important role in the prediction of adverse outcomes, including mortality, in a wide range of cardiovascular (CV) conditions. Because of complex RV geometry and load dependency of the RV functional parameters, conventional echocardiographic parameters such as RV fractional area change (FAC) and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE), have limited prognostic power in a large number of patients. RV longitudinal strain overcame the majority of these limitations, as it is angle-independent, less load-dependent, highly reproducible, and measure regional myocardial deformation. It has a high predictive value in patients with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, congenital heart disease, ischemic heart disease, pulmonary embolism, cardiomyopathies, and valvular disease. It enables detection of subclinical RV damage even when conventional parameters of RV systolic function are in the normal range. Even though cardiac magnetic resonance-derived RV longitudinal strain showed excellent predictive value, echocardiography-derived RV strain remains the method of choice for evaluation of RV mechanics primarily due to high availability. Despite a constantly growing body of evidence that support RV longitudinal strain evaluation in the majority of CV patients, its assessment has not become the part of the routine echocardiographic examination in the majority of echocardiographic laboratories. The aim of this clinical review was to summarize the current data about the predictive value of RV longitudinal strain in patients with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and valvular heart diseases.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; heart failure; longitudinal strain; mitral regurgitation; outcome; pulmonary hypertension; right ventricle; tricuspid regurgitation.
Copyright © 2021 Tadic, Nita, Schneider, Kersten, Buckert, Gonska, Scharnbeck, Reichart, Belyavskiy, Cuspidi and Rottbauer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
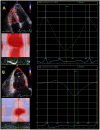
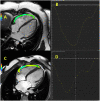
References
-
- Dong Y, Pan Z, Wang D, Lv J, Fang J, Xu R, et al. Prognostic value of cardiac magnetic resonance-derived right ventricular remodeling parameters in pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2020) 13:e010568. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.120.010568 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lyhne MD, Kabrhel C, Giordano N, Andersen A, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Zheng H, et al. The echocardiographic ratio tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion/pulmonary arterial systolic pressure predicts short-term adverse outcomes in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2021) 22:285–94. 10.1093/ehjci/jeaa243 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

