Test anxiety and procrastination in physiotherapy students
- PMID: 34222507
- PMCID: PMC8224484
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_851_20
Test anxiety and procrastination in physiotherapy students
Abstract
Background: Short-term academic procrastination may be accompanied by negative outcomes such as anxiety, stress, and depression. The current study aims to evaluate the two parameters of procrastination and test anxiety in physiotherapy students and explore whether a relationship exists between them.
Materials and methods: A descriptive, cross-sectional survey with a prospective study design was carried out over a period of 6 months. The study used a two-staged cluster sampling method: 220 undergraduate and postgraduate physiotherapy students from colleges in Mumbai and Navi Mumbai participated in the study, ensuring participation of students from each year of the course. The Westside Test Anxiety Scale was administered to evaluate test anxiety, and the Academic Procrastination Scale was used to evaluate procrastination. To illustrate the basic demographics of the participants, descriptive statistics were used. A correlation matrix was used to analyze the correlation between the two parameters.
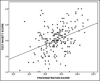
Results: The mean procrastination score of the physiotherapy students was 74.1. Amongst undergraduates, the highest procrastination was seen in the 3rd Bachelor of Physiotherapy students (mean = 76.7), whereas among postgraduates, the highest procrastination was seen in Master of Physiotherapy 1 students (mean = 75.7). The mean test anxiety score was 3, indicating moderately high test anxiety among students. There was a statistically significant, positive correlation between test anxiety score and procrastination score (P value = 0.000, Pearson's correlation co-efficient = 0.383).
Conclusion: Both test anxiety and the tendency to procrastinate were present among undergraduate and postgraduate physiotherapy students, in varying degrees. There was a positive correlation between the two factors.
Keywords: Academic success; Test Anxiety Scale; motivation; physiotherapy students; procrastination; time management.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sheikh YA. Higher education in India: Challenges and opportunities. J Educ Practice. 2017;8:39–42.
-
- Winston RB, Vahala ME, Nichols EC, Gillis ME, Wintrow M, Rome KD. Measure of college classroom climate: the college classroom environment scales. J Coll Student Develop. 1994;35:11–8.
-
- Al Qahtani MF. Associations between approaches to study, The learning environment, and academic achievement. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2015;10:56–65.
-
- Simon Cassidy. Learning styles: An overview of theories, models, and measures. Educ Psychol. 2004;24:4, 419–44.
-
- Newble DI, Entwistle NJ. Learning styles and approaches: Implications for medical education. Med Educ. 1986;20:162–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous