Diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF α-synuclein in prion disease in the context of rapidly progressive dementia
- PMID: 34222611
- PMCID: PMC8240124
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.12214
Diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF α-synuclein in prion disease in the context of rapidly progressive dementia
Abstract
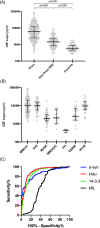
Introduction: Surrogate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of neurodegeneration still have a central role in the first-line screening of patients with suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). Recently, CSF α-synuclein, a marker of synaptic damage, showed a close to optimal performance in distinguishing between CJD and other neurodegenerative dementias.
Methods: We evaluated the diagnostic value of CSF α-synuclein in patients with prion disease, non-prion rapidly progressive dementias, and non-neurodegenerative controls. Additionally, we studied its distribution across the different prion disease subtypes and evaluated its association with survival.
Results: CSF α-synuclein levels were significantly higher in patients with prion disease than in the other groups but showed a lower diagnostic value than CSF total tau or 14-3-3. Moreover, CSF α-synuclein was significantly associated with survival in the whole prion cohort and the most frequent clinicopathological subtypes.
Discussion: In the clinical setting, CSF α-synuclein does not exceed the diagnostic performance of currently used surrogate markers, but it might constitute a robust prognostic indicator.
Keywords: Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease; alpha‐synuclein; cerebrospinal fluid; diagnosis; fatal familial insomnia; prognosis; rapidly progressive dementias.
© 2021 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S, et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol. 1999;46(2):224‐233. - PubMed
-
- Zerr I, Parchi P. Sporadic Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;153:155‐174. - PubMed
-
- Baiardi S, Capellari S, Bartoletti Stella A, et al. Unusual clinical presentations challenging the early clinical diagnosis of Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(4):1051‐1065. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
