Vascular pattern and radiological follow up in a case of pontine warning syndrome
- PMID: 34222700
- PMCID: PMC8242993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07369
Vascular pattern and radiological follow up in a case of pontine warning syndrome
Abstract
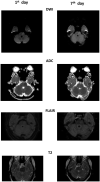
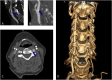
Pontine warning syndrome (PWS) is a condition characterized by crescendo transient ischemic attacks due to pontine ischemia. The reported case described a 72-year-old woman who presented repetitive sudden episodes of double vision, impaired balance, slurred speech and right-sided weakness. Neurological deficits lasted a few minutes-hours and disappeared during the first seven days after onset. On the 1st day, MRI revealed acute left paramedian pontine infarction with focal swelling. Supra-aortic vessel imagining revealed bilateral internal carotid stenosis of 50%; hypoplasia of the left vertebral artery. On the 7th day, MRI showed a tissue swelling reduction, and from that day, she had no symptoms. These clinical and radiological features were suggestive of PWS. Our patient presented a particular vascular pattern that could favour symptoms fluctuation. We performed a close MRI follow up and it allowed us to observe a clinical stabilization in association with edema reduction.
Keywords: Acute pontine ischemia; Carotid stenosis; MRI follow up; Pontine warning syndrome; Vertebral artery hypoplasia.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Muengtaweepongsa S., Singh N.N., Cruz-Flores S. Pontine warning syndrome: case series and review of literature. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010;19:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Farrar J., Donnan G.A. Capsular warning syndrome preceding pontine infarction. Stroke. 1993;24:762. - PubMed
-
- Saposnik G., Noel de Tilly L., Caplan L.R. Pontine warning syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 2008;65 - PubMed
-
- Tassi R., Cerase A., Acampa M., D’Andrea P., Guideri F., Lo Giudice G., Marotta G., Bracco S., Martini G. Stroke warning syndrome: 18 new cases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013;331:168–171. - PubMed
-
- Rahman Masum, Tadi Prasanna. Pons, Neuroanatomy. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

