Acquired pulmonary vein stenosis resulting in haemoptysis: a case series
- PMID: 34222784
- PMCID: PMC8243221
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytab235
Acquired pulmonary vein stenosis resulting in haemoptysis: a case series
Abstract
Background: Acquired pulmonary vein stenosis (PVS) is an infrequent complication of atrial fibrillation ablation that is often misdiagnosed due to predominant respiratory symptoms. It can result in pulmonary venous hypertension, with varying presentations, ranging from shortness of breath to haemoptysis.
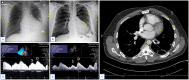
Case summary: We report two patients with a history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation treated with radiofrequency ablation and pulmonary vein (PV) isolation, who subsequently developed PVS. Case 1 initially presented with indolent symptoms of shortness of breath and cough. He was initially diagnosed with and treated for pneumonia. In contrast, Case 2 presented with massive haemoptysis, requiring intubation and intensive care unit admission. Both patients were eventually diagnosed with PVS by computed tomography. They were treated with PV angioplasty and stenting.
Discussion: While previously limited to the congenital heart disease population, PVS is occurring more frequently now in adult patients as a complication of ablation procedures. It is most effectively treated with angioplasty and stent implantation but has a high rate of recurrence.
Keywords: Ablation complication; Case report; Congenital heart disease; Haemoptysis; Pulmonary vein stenosis; Pulmonary vein stenting.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Partially reversible lung consolidation after revascularization of a total occlusion of both left pulmonary veins following ablation of atrial fibrillation: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2023 Feb 2;7(2):ytad057. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytad057. eCollection 2023 Feb. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36824364 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary vein stenosis requiring angioplasty or surgical treatment following pulmonary vein isolation: case series.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025 Feb 25;9(3):ytaf101. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaf101. eCollection 2025 Mar. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40061099 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of Pulmonary Vein Stenosis After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017 Jun;3(6):589-598. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Apr 26. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 29759432
-
Pulmonary vein stenosis complicating radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: A literature review.Respir Med. 2016 Aug;117:215-22. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.06.014. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27492534 Review.
-
Pulmonary veins stenosis after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation as the cause of haemoptysis: three cases and a literature review.Clin Respir J. 2018 Jan;12(1):3-9. doi: 10.1111/crj.12501. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 27216646 Review.
References
-
- Latson LA, Prieto LR.. Congenital and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Circulation 2007;115:103–108. - PubMed
-
- Saad EB, Rossillo A, Saad CP, Martin DO, Bhargava M, Erciyes D. et al. Pulmonary vein stenosis after radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: functional characterization, evolution, and influence of the ablation strategy. Circulation 2003;108:3102–3107. - PubMed
-
- Fender EA, Widmer RJ, Mahowald MK, Hodge DO, Packer DL, Holmes DR Jr.. Recurrent pulmonary vein stenosis after successful intervention: prognosis and management of restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2020;95:954–958. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
