Antibiotic resistance during and beyond COVID-19
- PMID: 34223149
- PMCID: PMC8210049
- DOI: 10.1093/jacamr/dlab052
Antibiotic resistance during and beyond COVID-19
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Education: The role of the first siderophore cephalosporin Fetcroja® (cefiderocol) in UK clinical practice: introduction; Antibiotic resistance during and beyond COVID-19; Education: An introduction to the core data for cefiderocol with reflections for a possible role within UK clinical practice; Education: A compassionate use of cefiderocol to treat osteomyelitis caused by an XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Compassionate use of cefiderocol for carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii prosthetic joint infection; Education: An overview from the author of 'Cefiderocol as rescue therapy for Acinetobacter baumannii and other carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative infections in intensive care unit patients'.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Aug 28;3(3):dlab109. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlab109. eCollection 2021 Sep. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2021. PMID: 34466802 Free PMC article.
Abstract
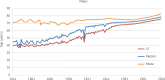
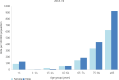
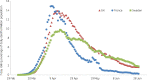
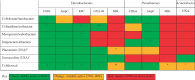
Antibiotics underpin the 'modern medicine' that has increased life expectancy, leading to societies with sizeable vulnerable elderly populations who have suffered disproportionately during the current COVID-19 pandemic. Governments have responded by shuttering economies, limiting social interactions and refocusing healthcare. There are implications for antibiotic resistance both during and after these events. During spring 2020, COVID-19-stressed ICUs relaxed stewardship, perhaps promoting resistance. Counterpoised to this, more citizens died at home and total hospital antibiotic use declined, reducing selection pressure. Restricted travel and social distancing potentially reduced community import and transmission of resistant bacteria, though hard data are lacking. The future depends on the vaccines now being deployed. Unequivocal vaccine success should allow a swift return to normality. Vaccine failure followed by extended and successful non-pharmaceutical suppression may lead to the same point, but only after some delay, and with indefinite travel restrictions; sustainability is doubtful. Alternatively, failure of vaccines and control measures may prompt acceptance that we must live with the virus, as in the prolonged 1889-94 'influenza' (or coronavirus OC43) pandemic. Vaccine failure scenarios, particularly those accepting 'learning to live with the virus', favour increased outpatient management of non-COVID-19 infections using oral and long t ½ antibiotics. Ultimately, all models-except those envisaging societal collapse-suggest that COVID-19 will be controlled and that hospitals will revert to pre-2020 patterns with a large backlog of non-COVID-19 patients awaiting treatment. Clearing this will increase workloads, stresses, nosocomial infections, antibiotic use and resistance. New antibiotics, including cefiderocol, are part of the answer.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Office for National Statistics. Mortality in England and Wales: Average Life Span, 2010. 2012. https://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20160110132605/http://www.ons....
-
- PHE. Chapter 1: Life Expectancy and Healthy Life Expectancy. 2017. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/health-profile-for-england/ch....
-
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population Ageing, 2017: Highlights. United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/agein....
-
- PHE, Department of Health and Social Care. Annual Epidemiological Commentary: Gram-Negative Bacteraemia, MRSA Bacteraemia, MSSA Bacteraemia and C. difficile Infections, up to and Including Financial Year April 2018 to March 2019. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
