COVID-19: a pandemic converged with global tobacco epidemic and widespread vaping-state of the evidence
- PMID: 34223886
- PMCID: PMC8344766
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgab061
COVID-19: a pandemic converged with global tobacco epidemic and widespread vaping-state of the evidence
Abstract
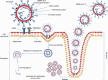
This review highlights the convergence of three global health challenges at a crossroad where the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) meets the tobacco epidemic and vaping. It begins with an overview of the current knowledge on the biology, pathophysiology and epidemiology of COVID-19. It then presents the state of smoking and vaping during the pandemic by summarizing the published data on prevalence, use patterns, product availability/accessibility, sales records and motivation to quit before and after the start of the pandemic. It highlights the state of evidence on the association of tobacco product use with COVID-19 infection and transmission rates, symptom severity and clinical outcomes. Also discussed are proposed biological mechanisms and behavioral factors that may modulate COVID-19 risk in tobacco product users. Furthermore, competing hypotheses on the protective effect of nicotine against COVID-19 as well as the claimed 'smokers' paradox' are discussed. Considerations and challenges of COVID-19 vaccination in tobacco product users are underscored. Collectively, the present data show an 'incomplete' but rapidly shaping picture on the association of tobacco product use and COVID-19 infection, disease course and clinical outcomes. Evidence is also growing on the mechanisms by which tobacco product use may contribute to COVID-19 pathophysiology. Although we await definitive conclusions on the relative risk of COVID-19 infection in tobacco product users, compelling data confirm that many comorbidities associated with/caused by smoking predispose to COVID-19 infection, severe disease and poor prognosis. Additionally, it is becoming increasing clear that should smokers get the disease, they are more likely to have serious health consequences.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2019) Who Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2019: Offer Help to Quit Tobacco Use. https://www.who.int/tobacco/global_report/en/ (18 June 2021, date last accessed).
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services (2018) Surgeon General’s Advisory on E-Cigarette Use Among Youth. https://e-cigarettes.surgeongeneral.gov/documents/surgeon-generals-advis... (18 June 2021, date last accessed).
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2018) FDA Takes New Steps to Address Epidemic of Youth E-Cigarette Use, Including a Historic Action Against More Than 1,300 Retailers and 5 Major Manufacturers for Their Roles Perpetuating Youth Access. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-takes-new-steps-... (11 September 2018, date last accessed).

