Mortality Among Persons Entering HIV Care Compared With the General U.S. Population : An Observational Study
- PMID: 34224262
- PMCID: PMC8453103
- DOI: 10.7326/M21-0065
Mortality Among Persons Entering HIV Care Compared With the General U.S. Population : An Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Understanding advances in the care and treatment of adults with HIV as well as remaining gaps requires comparing differences in mortality between persons entering care for HIV and the general population.
Objective: To assess the extent to which mortality among persons entering HIV care in the United States is elevated over mortality among matched persons in the general U.S. population and trends in this difference over time.
Design: Observational cohort study.
Setting: Thirteen sites from the U.S. North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design.
Participants: 82 766 adults entering HIV clinical care between 1999 and 2017 and a subset of the U.S. population matched on calendar time, age, sex, race/ethnicity, and county using U.S. mortality and population data compiled by the National Center for Health Statistics.
Measurements: Five-year all-cause mortality, estimated using the Kaplan-Meier estimator of the survival function.
Results: Overall 5-year mortality among persons entering HIV care was 10.6%, and mortality among the matched U.S. population was 2.9%, for a difference of 7.7 (95% CI, 7.4 to 7.9) percentage points. This difference decreased over time, from 11.1 percentage points among those entering care between 1999 and 2004 to 2.7 percentage points among those entering care between 2011 and 2017.
Limitation: Matching on available covariates may have failed to account for differences in mortality that were due to sociodemographic factors rather than consequences of HIV infection and other modifiable factors.
Conclusion: Mortality among persons entering HIV care decreased dramatically between 1999 and 2017, although those entering care remained at modestly higher risk for death in the years after starting care than comparable persons in the general U.S. population.
Primary funding source: National Institutes of Health.
Figures


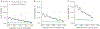
Comment in
-
HIV: Closing the Mortality Gap.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Sep;174(9):1311-1312. doi: 10.7326/M21-2586. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34224260 No abstract available.
References
-
- CD4+ Count–Guided Interruption of Antiretroviral Treatment. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006November30;355(22):2283–96. - PubMed
-
- Clotet B, Feinberg J, van Lunzen J, Khuong-Josses M-A, Antinori A, Dumitru I, et al.Once-daily dolutegravir versus darunavir plus ritonavir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (FLAMINGO): 48 week results from the randomised open-label phase 3b study. The Lancet. 2014June;383(9936):2222–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY013707/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010176/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM133807/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020790/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI131895/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA037788/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CP001004/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI124794/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007587/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI157758/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R34 DA045592/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI093197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI125087/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P2C HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG053100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD093602/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
