Analysis of regulatory effect of miR-149-5p on Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 of pericytes and its neuroprotective molecular mechanism after acute cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats
- PMID: 34224319
- PMCID: PMC8806611
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1947167
Analysis of regulatory effect of miR-149-5p on Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 of pericytes and its neuroprotective molecular mechanism after acute cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats
Abstract
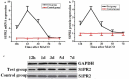
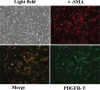
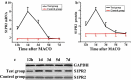
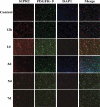
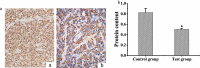
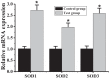
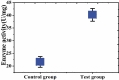
To investigate the effect of miR-149-5p on sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) expression level and contents of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the pericytes after acute cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats, so as to clarify the neuroprotective molecular mechanism induced by miR-149-5p and provide references for the treatment of neurological diseases, 60 male SD rats aged 7-8 weeks were selected and divided randomly into test group (establishing middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model) and control group (no modeling). Rat pericytes and peripheral cerebral infarction tissues were collected 12 h, 1 d, 3 d, 5 d, and 7 d after MCAO modeling, respectively. The pericytes were identified by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and transfected with miR-149-5p. Fluorescence quantitative PCR (FQPCR) and Western blot were adopted to detect S1PR2 expression level. The expression of S1PR2 in MCAO model rats was detected by IFA. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) were used to detect the changes of MMP9 protein and mRNA levels of SOD1, SOD2, and SOD3 in brain tissue. The results showed that mRNA level and protein expression level of S1PR2 in the test group were higher than those in the control group three days after MCAO modeling (P < 0.05); the expression of S1PR2 increased 12 h after MCAO modeling and returned to the normal level on the 5th day, and the content of MMP9 protein in brain tissue of the test group was significantly lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05); the mRNA levels and SODs activity of SOD1, SOD2, and SOD3 in the test group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Therefore, miR-149-5p played a neuroprotective role by regulating S1PR2 to change the expression levels of SODS and MMP9.
Keywords: Mir-149-5p; S1PR2; acute cerebral ischemia reperfusion; mmp9 protein; neuroprotection; pericytes.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-149-5p regulates blood-brain barrier permeability after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats by targeting S1PR2 of pericytes.FASEB J. 2018 Jun;32(6):3133-3148. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701121R. Epub 2018 Jan 18. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29401609
-
MicroRNA-182-5p attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting Toll-like receptor 4.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Nov 2;505(3):677-684. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.165. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30292407
-
miR-211-5p alleviates focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by down-regulating the expression of COX2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;177:113983. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113983. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32311346
-
MiR-155-5p accelerates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via targeting DUSP14 by regulating NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(3):1408-1419. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20198. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32096190
-
LncRNA SNHG4 Attenuates Inflammatory Responses by Sponging miR-449c-5p and Up-Regulating STAT6 in Microglial During Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Sep 11;14:3683-3695. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S245445. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982175 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Regulating the S1PR2/TLR4/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway via m6A Methylation of lncRNA H19.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024;21(1):64-73. doi: 10.2174/0115672026294183240207115956. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 38409728
-
Alleviating early demyelination in ischaemia/reperfusion by inhibiting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 could protect visual function from impairment.Brain Pathol. 2023 Sep;33(5):e13161. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13161. Epub 2023 May 4. Brain Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37142391 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Forkhead box O1-aquaporin 5 axis mitigates neuropathic pain in a CCI rat model through inhibiting astrocytic and microglial activation.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):8567-8580. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2053032. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35324416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howell JA, Bidwell GL.. Targeting the NF-κB pathway for therapy of ischemic stroke. Ther Deliv. 2020;11(2):113–123. - PubMed
-
- Darcourt J, Withayasuk P, Vukasinovic I, et al. Predictive value of susceptibility vessel sign for arterial recanalization and clinical improvement in ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2019;50(2):512–515. . - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Cai H, Lin M, et al. MicroRNA-107 prevents amyloid-beta induced blood-brain barrier disruption and endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting Endophilin-1. Exp Cell Res. 2016;343(2):248–257. . - PubMed
-
- De Queiroz KB, Pereira TD, Araujo MS, et al. Resveratrol acts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective in an infant rat model of pneumococcal meningitis by modulating the hippocampal miRNome. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(12):8869–8884. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
