The mediating role of emotional eating in the relationship between perceived stress and dietary intake quality in Hispanic/Latino adolescents
- PMID: 34225165
- PMCID: PMC8380719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2021.101537
The mediating role of emotional eating in the relationship between perceived stress and dietary intake quality in Hispanic/Latino adolescents
Abstract
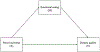
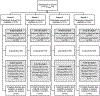
Obesity rates have steadily increased over the past three decades, and large racial/ethnic disparities in childhood obesity rates-specifically for Hispanic/Latino youth-highlight the major need for identifying and examining key mechanisms of obesogenic behaviors for this at-risk population. This study investigates the relationship between stress and dietary quality in Hispanic/Latino adolescents and seeks to determine the mediating role of emotional eating as a behavioral mechanism. Baseline data from 169 adolescents enrolled in the Imagine HEALTH trial were used to investigate these relationships. Perceived stress and emotional eating were assessed with age-validated questionnaires, and dietary quality was measured via 24-hour recall dietary assessments (later calculated as individual Healthy Eating Index-2015 scores). Nonparametric bootstrapping was used to test the primary hypothesis that emotional eating partially or fully mediates the relationship between perceived stress and dietary quality in this sample, and to test the significance of the mediating effect. Results indicate that emotional eating partially mediates the relationship between perceived stress and dietary quality. The total effect of perceived stress scores on dietary quality scores was -0.24 (p = .006); the direct effect of perceived stress scores on dietary quality scores (controlling for emotional eating scores) was -0.16 (p = .107), and the mediating (indirect) effect of emotional eating was -0.09 (p = .001). The proportion of mediation was 0.36 (36%) (p = .008). This study identifies an important mechanism of obesogenic behavior and can be used to inform future obesity prevention and intervention strategies tailored for the Hispanic/Latino adolescent population.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02088294.
Keywords: Adolescent; Diet; Emotional eating; Hispanic; Latino; Stress.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev. 2008;9(5):474–488. - PubMed
-
- Reilly JJ, Kelly J. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011;35(7):891–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous