Fièvre persistante, aphasie et douleur à la jambe chez un homme de 59 ans
- PMID: 34226270
- PMCID: PMC8248568
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.201491-f
Fièvre persistante, aphasie et douleur à la jambe chez un homme de 59 ans
Conflict of interest statement
Intérêts concurrents: Aucun déclaré.
Figures
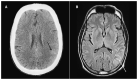
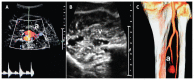
References
-
- Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. ; American Heart Association Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and Stroke Council. Infective endocarditis in adults: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015;132:1435–86. - PubMed
-
- Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: the task force for the management of infective endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J 2015;36: 3075–128. - PubMed
-
- Fernández Guerrero ML, Goyenechea A, Verdejo C, et al. . Enterococcal endocarditis on native and prosthetic valves: a review of clinical and prognostic factors with emphasis on hospital-acquired infections as a major determinant of outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007;86:363–77. - PubMed
-
- Pericàs JM, Corredoira J, Moreno A, et al. Hospital Clínic and Hospital Lucus Augusti Infective Endocarditis Investigators. Relationship between Enterococcus faecalis infective endocarditis and colorectal neoplasm: preliminary results from a cohort of 154 patients. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2017;70:451–8. - PubMed
-
- van Es N, Le Gal G, Otten H-M, et al. . Screening for occult cancer in patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Ann Intern Med 2017;167:410–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
