[Determination of three diphenyl ether herbicides in rice by magnetic solid phase extraction using Fe3O4@MOF-808 coupled with high performance liquid chromatography]
- PMID: 34227312
- PMCID: PMC9403814
- DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.06007
[Determination of three diphenyl ether herbicides in rice by magnetic solid phase extraction using Fe3O4@MOF-808 coupled with high performance liquid chromatography]
Abstract
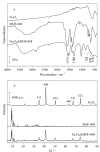
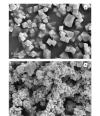
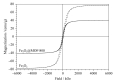
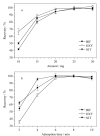
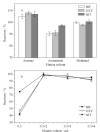
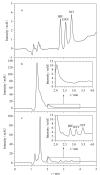
The complex matrix of rice samples and the small amount of the target analytes in the sample necessitate an effective pretreatment process to enrich the target analytes and minimize matrix interference before instrumental analysis. Magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) is a dispersive solid phase extraction technique which allows for the rapid separation of sorbents from the sample solution under an external magnetic field. Compared with other traditional solid phase extraction methods, MSPE has the advantages of convenient operation, minimal interference and absence of column pressure. In this work, a metal organic framework composite (Fe3O4@MOF-808) was synthesized by a facile solvothermal method for using as an effective adsorbent to concentrate nitrofen (NIT), oxyfluorfen (OXY) and bifenox (BIF) in rice samples. Based on the pretreatment, a method was developed by coupling with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection (HPLC-UV). The prepared material was characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy and vibrating sample magnetometry measurements for determining its functional groups, morphology and magnetic strength. The results showed that MOF-808 has a regular octahedral morphology and well-dispersed, and the particle size of the material ranged from 400 to 500 nm with a smooth surface. The spherical Fe3O4 particles were uniformly attached to the surface of the octahedral MOF-808 crystals. The maximum saturation magnetization of this composite was 40.35 emu/g which is lower than the saturation magnetization Fe3O4 (78.26 emu/g) but still sufficient for the requirements of MSPE. The prepared Fe3O4@MOF-808 was used in the MSPE of three diphenyl ether herbicides (Des) in rice. As is well known, the key factors influencing MSPE are the adsorption and elution processes. In order to establish the optimal extraction conditions, the adsorption parameters (adsorbent amount, extraction time, elution solvent and elution volume) were investigated in detail. A 15 mL mixed standard solution was used in the experiment, and the concentrations of the three Des were 65 ng/mL. All the experiments were performed in parallel three times. The effects of the dosages of Fe3O4@MOF-808 (10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 mg), adsorption time (2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 min), elution solvents (acetone, acetonitrile and methanol) and elution volume (0.5 mL, 0.5 mL×2, 0.5 mL×3, 0.5 mL×4) were investigated. The Des could be adsorbed completely by using 25 mg of Fe3O4@MOF-808 for no more than 6 min. Elution was performed with 0.5 mL×2 of methanol. Various parameters such as limits of detection (LODs), limits of quantification (LOQs), accuracy and precision of the method were evaluated. The method showed good linearity in the range of 2-300 μg/L (r > 0.998). The LODs and LOQs were 0.6, 0.6, 0.4 μg/kg and 2.0, 2.0,1.5 μg/kg for NIT, OXY, BIF respectively. At spiked levels of 5, 10 and 20 μg/kg, the recoveries ranged from 87.3% to 96.7% with relative standard deviations (RSDs) less than 10.8%. The enrichment factors (EFs) of the method for the three Des were between 25 and 29. The method was applied to the pretreatment of the three Des in real samples, and none of the Des could be detected at any of the samples. This method had a lower LOD than that of the national standard method, but its LOD and recovery were similar to those of other reference methods. In summary, the developed method has the advantages of operational simplicity, rapidity and accuracy, and it is suitable for the analysis of herbicide residues in rice samples.
利用溶剂热法构筑了Fe3O4@MOF-808吸附剂,将其用于大米中除草醚(NIT)、乙氧氟草醚(OXY)和甲羧除草醚(BIF)3种二苯醚类除草剂的富集,结合高效液相色谱法,建立了大米中该类除草剂的分析方法。研究通过傅里叶变换红外光谱、X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜以及振动样品磁强计对构筑的磁性吸附剂的结构、表面形貌及磁强度进行表征。表征结果显示,球形的Fe3O4纳米颗粒与八面体形貌的MOF-808成功复合,Fe3O4@MOF-808饱和磁化强度可达40.35 emu/g,可以满足磁性固相萃取的需求;对吸附剂用于大米中3种二苯醚类除草剂富集的磁性固相萃取条件(吸附剂用量、吸附时间、洗脱溶剂种类以及洗脱体积)进行了优化。优化结果显示,25 mg吸附剂在6 min内即可达到对目标物的完全吸附,洗脱溶剂采用0.5 mL×2的甲醇。在最优的磁性固相萃取条件下,结合高效液相色谱-紫外检测法,建立了大米中3种二苯醚类除草剂的分析方法。方法在2~300 μg/L范围内线性关系良好(r > 0.998), NIT、OXY、BIF的检出限和定量限依次为0.6、0.6、0.4 μg/kg和2.0、2.0、1.5 μg/kg,在5、10和20 μg/kg 3个加标水平下的回收率为87.3%~96.7%,相对标准偏差不超过10.8%,且富集因子在25~29之间。将所建方法用于大米中NIT、OXY、BIF的分析,各样品均未检出这3种二苯醚类除草剂。该方法具有操作简单、快速、准确的特点,适用于大米样品中除草剂的残留分析。
Keywords: diphenyl ether herbicides (Des); high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE); metal organic frameworks (MOFs); rice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Determination of seven phenoxy acid herbicides in water by dispersive solid phase extraction-ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on cationic metal-organic framework mixed matrix membrane].Se Pu. 2021 Aug;39(8):896-904. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.01006. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34212590 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Determination of four fungicides in water by magnetic solid phase extraction-ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using covalent organic framework material].Se Pu. 2022 Nov;40(11):988-997. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.08023. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 36351807 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Determination of 10 fluoroquinolones residues in aquatic products by accelerated solvent extraction, magnetic solid-phase extraction, and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2020 Dec 8;38(12):1413-1422. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05002. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213256 Chinese.
-
[Research progress in the application of magnetic solid phase extraction based on carbon based magnetic materials in food analysis].Se Pu. 2021 Apr 8;39(4):368-375. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05038. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227756 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
[Research progress in application of metal-organic framework-derived materials to sample pretreatment].Se Pu. 2021 Sep;39(9):941-949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.05017. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34486833 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Fluorescent Molecular Imprinted Sensor Based on Carbon Quantum Dot for Nitrofen Detection in Water Sample.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Mar 20;17(6):816. doi: 10.3390/polym17060816. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292707 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in solid-phase extraction for bisphenols in environmental samples].Se Pu. 2021 Aug;39(8):835-844. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.02035. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34212584 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Wu C Y, Gu F, Bai L, et al.. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2015,34(9):1014
- 吴春英, 谷风, 白鹭, et al.. 分析试验室, 2015,34(9):1014 - PubMed
-
- Xu J Y, Shi Y, Gao B B, et al.. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2019,21(4):468
- 徐江艳, 施瑛, 高贝贝, et al.. 农药学学报, 2019,21(4):468
-
- GB/T 2763-2019.
-
- Wang H X, Li Y Q, Yong L, et al.. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2007,25(4):536 - PubMed
- 王和兴, 黎源倩, 雍莉, et al.. 色谱, 2007,25(4):536
-
- Jin B H, Xie L Q, Wu W D, et al.. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2008,27(6):75
- 靳保辉, 谢丽琪, 吴卫东, et al.. 分析试验室, 2008,27(6):75
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials