Connexins in the development and physiology of stem cells
- PMID: 34227910
- PMCID: PMC8794508
- DOI: 10.1080/21688370.2021.1949242
Connexins in the development and physiology of stem cells
Abstract
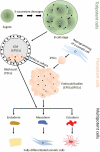
Connexins (Cxs) form gap junction (GJ) channels linking vertebrate cells. During embryogenesis, Cxs are expressed as early as the 4-8 cell stage. As cells differentiate into pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) and during gastrulation, the Cx expression pattern is adapted. Knockdown of Cx43 and Cx45 does not interfere with embryogenic development until the blastula stage, questioning the role of Cxs in PSC physiology and development. Studies in cultivated and induced PSCs (iPSCs) showed that Cx43 is essential for the maintenance of self-renewal and the expression of pluripotency markers. It was found that the role of Cxs in PSCs is more related to regulation of transcription or cell-cell adherence than to formation of GJ channels. Furthermore, a crucial role of Cxs for the self-renewal and differentiation was shown in cultivated adult mesenchymal stem cells. This review aims to highlight aspects that link Cxs to the function and physiology of stem cell development.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
References
-
- Bader A, Bintig W, Begandt D, Klett A, Siller IG, Gregor C, et al. Adenosine receptors regulate gap junction coupling of the human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells hCMEC/D3 by Ca2+ influx through cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. J Physiol. 2017;595(8):2497–2517. PubMed-ID: 28075020. PMCID: PMC5390872. doi:10.1113/jp273150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schadzek P, Schlingmann B, Schaarschmidt F, Lindner J, Koval M, Heisterkamp A, et al. The cataract related mutation N188T in human connexin46 (hCx46) revealed a critical role for residue N188 in the docking process of gap junction channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1858(1):57–66. PubMed-ID: 26449341. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous