CCN proteins in the musculoskeletal system: current understanding and challenges in physiology and pathology
- PMID: 34228239
- PMCID: PMC8642527
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-021-00631-5
CCN proteins in the musculoskeletal system: current understanding and challenges in physiology and pathology
Abstract
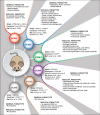
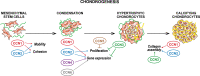
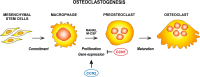
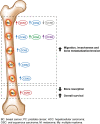
The acronym for the CCN family was recently revised to represent "cellular communication network". These six, small, cysteine-enriched and evolutionarily conserved proteins are secreted matricellular proteins, that convey and modulate intercellular communication by interacting with structural proteins, signalling factors and cell surface receptors. Their role in the development and physiology of musculoskeletal system, constituted by connective tissues where cells are interspersed in the cellular matrix, has been broadly studied. Previous research has highlighted a crucial balance of CCN proteins in mesenchymal stem cell commitment and a pivotal role for CCN1, CCN2 and their alter ego CCN3 in chondrogenesis and osteogenesis; CCN4 plays a minor role and the role of CCN5 and CCN6 is still unclear. CCN proteins also participate in osteoclastogenesis and myogenesis. In adult life, CCN proteins serve as mechanosensory proteins in the musculoskeletal system providing a steady response to environmental stimuli and participating in fracture healing. Substantial evidence also supports the involvement of CCN proteins in inflammatory pathologies, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as in cancers affecting the musculoskeletal system and bone metastasis. These matricellular proteins indeed show involvement in inflammation and cancer, thus representing intriguing therapeutic targets. This review discusses the current understanding of CCN proteins in the musculoskeletal system as well as the controversies and challenges associated with their multiple and complex roles, and it aims to link the dispersed knowledge in an effort to stimulate and guide readers to an area that the writers consider to have significant impact and relevant potentialities.
Keywords: Bone metastasis; Bone sarcomas; Cellular communication network; Osteoarthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Skeletogenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

