Rhinovirus spread in children during the COVID-19 pandemic despite social restrictions-A nationwide register study in Finland
- PMID: 34228369
- PMCID: PMC8426983
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27180
Rhinovirus spread in children during the COVID-19 pandemic despite social restrictions-A nationwide register study in Finland
Abstract
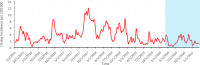
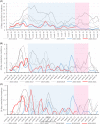
Social restrictions during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic strongly affected the epidemiology of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). As rhinovirus seemed to spread despite the restrictions, we aimed to analyze rhinovirus epidemiology in children during the pandemic. This register-based study used data from the Finnish Infectious Disease Register. Nationwide rhinovirus findings from July 2015 to March 2021 were included and stratified by age (0-4, 5-9, and 10-14). Cumulative 14-day incidence per 100000 children was calculated. Four thousand five hundred and seventy six positive rhinovirus findings were included, of which 3788 (82.8%) were among children aged 0-4. The highest recorded incidence was 36.2 among children aged 0-4 in October 2017. The highest recorded incidence during the pandemic period was 13.6 in November 2020. The impact of the restrictions was mostly seen among children aged 0-4 years of age in weeks 14-22 in 2020. The incidence has since remained near reference levels in all age groups. Strict restrictions temporarily interrupted the circulation of rhinovirus in spring 2020. Rhinovirus incidence returned to normal levels soon after the harsh restrictions were lifted. These looser social restrictions prevented RSV and influenza seasons but failed to prevent the spread of rhinovirus.
Keywords: epidemiology; nonpharmaceutical interventions; rhinovirus; surveillance.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kuitunen I, Artama M, Mäkelä L, Backman K, Heiskanen‐Kosma T, Renko M. Effect of social distancing due to the COVID‐19 pandemic on the incidence of viral respiratory tract infections in children in Finland during early 2020. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39(12):e423‐e427. 10.1097/INF.0000000000002845 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haapanen M, Renko M, Artama M, Kuitunen I. The impact of the lockdown and the re‐opening of schools and day cares on the epidemiology of SARS‐CoV‐2 and other respiratory infections in children—a nationwide register study in Finland. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;34:100807. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100807 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

