Inhibition of NFAM1 suppresses phospho-SAPK/JNK signaling during osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption
- PMID: 34228377
- PMCID: PMC8479865
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.30076
Inhibition of NFAM1 suppresses phospho-SAPK/JNK signaling during osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption
Abstract
We have recently demonstrated NFAT activating protein with ITAM motif 1 (NFAM1) signaling increases osteoclast (OCL) formation/bone resorption associated with the Paget's disease of bone, however, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the NFAM1 regulation of OCL differentiation and bone resorption remains unclear. Here, we showed that RANK ligand stimulation enhances NFAM1 expression in preosteoclast cells. Conditioned media collected from RANKL stimulated RAW264.7 NFAM1 knockdown (KD) stable cells showed inhibition of interleukin-6 (2.5-fold), tumour necrosis factor-α (2.2-fold) and CXCL-5 (3-fold) levels compared to wild-type (WT) cells. Further, RANKL stimulation significantly increased p-STAT6 expression (5.5-fold) in WT cells, but no significant effect was observed in NFAM1-KD cells. However, no changes were detected in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 levels in either of cell groups. Interestingly, NFAM1-KD suppressed the RANKL stimulated c-fos, p-c-Jun and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity in preosteoclasts. We further showed that the suppression of JNK activity is through inhibition of p-SAPK/JNK in these cells. In addition, NFATc1 expression, a critical transcription factor associated with osteoclastogenesis is significantly inhibited in NFAM1-KD preosteoclast cells. Interestingly, NFAM1 inhibition suppressed the OCL differentiation and bone resorption capacity in mouse bone marrow cell cultures. We also demonstrated inhibition of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase expression in RANKL stimulated NFAM1-KD preosteoclast cells. Thus, our results suggest that NFAM1 control SAPK/JNK signaling to modulate osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption.
Keywords: JNK activity; NFAM1; NFATc1; Osteoclast; c-fos; p-SAPK/JNK.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

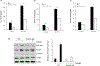

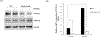
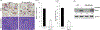

Similar articles
-
NFAM1 signaling enhances osteoclast formation and bone resorption activity in Paget's disease of bone.Bone. 2017 Aug;101:236-244. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.05.013. Epub 2017 May 12. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28506889 Free PMC article.
-
Constant hypoxia inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by regulating phosphorylation of JNK and IκBα.Inflamm Res. 2019 Feb;68(2):157-166. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1209-9. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 30604211
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Proteasome inhibition suppress microgravity elevated RANK signaling during osteoclast differentiation.Cytokine. 2020 Jan;125:154821. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154821. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31470364
-
Kalkitoxin Reduces Osteoclast Formation and Resorption and Protects against Inflammatory Bone Loss.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2303. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052303. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669069 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent advances of NFATc1 in rheumatoid arthritis-related bone destruction: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Mol Med. 2024 Feb 3;30(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00788-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38310228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFAM1 Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse and Human Monocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:773445. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.773445. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095847 Free PMC article.
-
Ononin Inhibits Tumor Bone Metastasis and Osteoclastogenesis By Targeting Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Breast Cancer.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Dec 16;7:0553. doi: 10.34133/research.0553. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 39687715 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Health and Disease.MedComm (2020). 2025 Mar 30;6(4):e70152. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70152. eCollection 2025 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40166646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad R, Kochumon S, Chandy B, Shenouda S, Koshy M, Hasan A, Arefanian H, Al-Mulla F, Sindhu S. 2019. TNF-alpha Drives the CCL4 Expression in Human Monocytic Cells: Involvement of the SAPK/JNK and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 52:908–921. - PubMed
-
- Asagiri M, Takayanagi H. 2007. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 40:251–64. - PubMed
-
- David JP, Sabapathy K, Hoffmann O, Idarraga MH, Wagner EF. 2002. JNK1 modulates osteoclastogenesis through both c-Jun phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Cell Sci 115:4317–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

