In Vivo Induction of P-Glycoprotein Function can be Measured with [18F]MC225 and PET
- PMID: 34228458
- PMCID: PMC8383301
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00302
In Vivo Induction of P-Glycoprotein Function can be Measured with [18F]MC225 and PET
Abstract
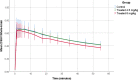
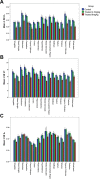
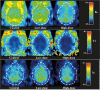
P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) is an efflux pump located at the blood-brain barrier (BBB) that contributes to the protection of the central nervous system by transporting neurotoxic compounds out of the brain. A decline in P-gp function has been related to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. P-gp inducers can increase the P-gp function and are considered as potential candidates for the treatment of such disorders. The P-gp inducer MC111 increased P-gp expression and function in SW480 human colon adenocarcinoma and colo-320 cells, respectively. Our study aims to evaluate the P-gp inducing effect of MC111 in the whole brain in vivo, using the P-gp tracer [18F]MC225 and positron emission tomography (PET). Eighteen Wistar rats were treated with either vehicle solution, 4.5 mg/kg of MC111 (low-dose group), or 6 mg/kg of MC111 (high-dose group). Animals underwent a 60 min dynamic PET scan with arterial-blood sampling, 24 h after treatment with the inducer. Data were analyzed using the 1-tissue-compartment model and metabolite-corrected plasma as the input function. Model parameters such as the influx constant (K1) and volume of distribution (VT) were calculated, which reflect the in vivo P-gp function. P-gp and pregnane xenobiotic receptor (PXR) expression levels of the whole brain were assessed using western blot. The administration of MC111 decreased K1 and VT of [18F]MC225 in the whole brain and all of the selected brain regions. In the high-dose group, whole-brain K1 was decreased by 34% (K1-high-dose = 0.20 ± 0.02 vs K1-control = 0.30 ± 0.02; p < 0.001) and in the low-dose group by 7% (K1-low-dose = 0.28 ± 0.02 vs K1-control = 0.30 ± 0.02; p = 0.42) compared to controls. Whole-brain VT was decreased by 25% in the high-dose group (VT-high-dose = 5.92 ± 0.41 vs VT-control = 7.82 ± 0.38; p < 0.001) and by 6% in the low-dose group (VT-low-dose = 7.35 ± 0.38 vs VT-control = 7.82 ± 0.37; p = 0.38) compared to controls. k2 values did not vary after treatment. The treatment did not affect the metabolism of [18F]MC225. Western blot studies using the whole-brain tissue did not detect changes in the P-gp expression, however, preliminary results using isolated brain capillaries found an increasing trend up to 37% in treated rats. The decrease in K1 and VT values after treatment with the inducer indicates an increase in the P-gp functionality at the BBB of treated rats. Moreover, preliminary results using brain endothelial cells also sustained the increase in the P-gp expression. In conclusion, the results verify that MC111 induces P-gp expression and function at the BBB in rats. An increasing trend regarding the P-gp expression levels is found using western blot and an increased P-gp function is confirmed with [18F]MC225 and PET.
Keywords: ABC transporters; P-glycoprotein; P-gp inducers; brain Imaging; efflux transporters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetic Modeling of [18F]MC225 for Quantification of the P-Glycoprotein Function at the Blood-Brain Barrier in Non-Human Primates with PET.Mol Pharm. 2020 Sep 8;17(9):3477-3486. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00514. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32787277 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-response assessment of cerebral P-glycoprotein inhibition in vivo with [18F]MC225 and PET.J Control Release. 2022 Jul;347:500-507. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.026. Epub 2022 May 20. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35588934
-
Quantification of P-glycoprotein function at the human blood-brain barrier using [18F]MC225 and PET.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Nov;50(13):3917-3927. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06363-5. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37552369 Free PMC article.
-
Positron emission tomography studies on binding of central nervous system drugs and P-glycoprotein function in the rodent brain.Mol Imaging Biol. 2005 Jan-Feb;7(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s11307-005-0951-x. Mol Imaging Biol. 2005. PMID: 15912274 Review.
-
Radiopharmaceuticals for assessing ABC transporters at the blood-brain barrier.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;97(4):362-71. doi: 10.1002/cpt.73. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25669763 Review.
Cited by
-
Measurement of cyclosporin induced changes in P-glycoprotein function at the human blood-brain barrier using [18F]MC225 and PET.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 May 8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07320-0. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40338304
-
Cardiac PET Imaging of ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters: Opportunities and Challenges.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;16(12):1715. doi: 10.3390/ph16121715. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging blood-brain barrier disruption in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 17;15:1144036. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1144036. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37009464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First clinical assessment of [18F]MC225, a novel fluorine-18 labelled PET tracer for measuring functional P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier.Ann Nucl Med. 2021 Nov;35(11):1240-1252. doi: 10.1007/s12149-021-01666-9. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Ann Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 34368924
-
Dysfunction of ABC Transporters at the Surface of BBB: Potential Implications in Intractable Epilepsy and Applications of Nanotechnology Enabled Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(9):735-756. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220817115003. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35980054 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

