Phycobilisome breakdown effector NblD is required to maintain the cellular amino acid composition during nitrogen starvation
- PMID: 34228497
- PMCID: PMC8765419
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00158-21
Phycobilisome breakdown effector NblD is required to maintain the cellular amino acid composition during nitrogen starvation
Abstract
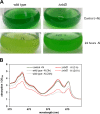
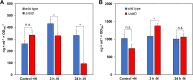
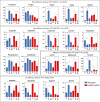
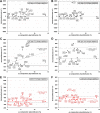
Small proteins are critically involved in the acclimation response of photosynthetic cyanobacteria to nitrogen starvation. NblD is the 66-amino-acid effector of nitrogen-limitation-induced phycobilisome breakdown, which is believed to replenish the cellular amino acid pools. To address the physiological functions of NblD, the concentrations of amino acids, intermediates of the arginine catabolism pathway and several organic acids were measured during the response to nitrogen starvation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 wild type and in an nblD deletion strain. A characteristic signature of metabolite pool composition was identified, which shows that NblD-mediated phycobilisome degradation is required to maintain the cellular amino acid and organic acid pools during nitrogen starvation. Specific deviations from the wild type suggest wider-reaching effects that also affect such processes as redox homeostasis via glutathione and tetrapyrrole biosynthesis, both of which are linked to the strongly decreased glutamate pool, and transcriptional reprogramming via an enhanced concentration of 2-oxoglutarate, the metabolite co-regulator of the NtcA transcription factor. The essential role played by NblD in metabolic homeostasis is consistent with the widespread occurrence of NblD throughout the cyanobacterial radiation and the previously observed strong positive selection for the nblD gene under fluctuating nitrogen supply. Importance Cyanobacteria play important roles in the global carbon and nitrogen cycles. In their natural environment, these organisms are exposed to fluctuating nutrient conditions. Nitrogen starvation induces a coordinated nitrogen-saving program that includes the breakdown of nitrogen-rich photosynthetic pigments, particularly phycobiliproteins. The small protein NblD was recently identified as an effector of phycobilisome breakdown in cyanobacteria. In this study, we demonstrate that the NblD-mediated degradation of phycobiliproteins is needed to sustain cellular pools of soluble amino acids and other crucial metabolites. The essential role played by NblD in metabolic homeostasis explains why genes encoding this small protein are conserved in almost all members of cyanobacterial radiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of a small protein factor involved in the coordinated degradation of phycobilisomes in cyanobacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Feb 2;118(5):e2012277118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012277118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33509926 Free PMC article.
-
NblA1/A2-Dependent Homeostasis of Amino Acid Pools during Nitrogen Starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Metabolites. 2014 Jun 30;4(3):517-31. doi: 10.3390/metabo4030517. Metabolites. 2014. PMID: 24983765 Free PMC article.
-
Alanine dehydrogenase activity is required for adequate progression of phycobilisome degradation during nitrogen starvation in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(14):5258-65. doi: 10.1128/JB.00209-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16816198 Free PMC article.
-
The phycobilisome, a light-harvesting complex responsive to environmental conditions.Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):725-49. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.725-749.1993. Microbiol Rev. 1993. PMID: 8246846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ammonium assimilation in cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res. 2005;83(2):135-50. doi: 10.1007/s11120-004-2082-7. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 16143848 Review.
Cited by
-
The Global Influence of Sodium on Cyanobacteria in Resuscitation from Nitrogen Starvation.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;12(2):159. doi: 10.3390/biology12020159. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829438 Free PMC article.
-
Site-2 Protease Slr1821 Regulates Carbon/Nitrogen Homeostasis during Ammonium Stress Acclimation in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 1;24(7):6606. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076606. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047577 Free PMC article.
-
The primary carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria and its regulation.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jul 5;15:1417680. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1417680. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39036361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Small Proteins Adjust the Metabolism of Cyanobacteria Under Stress: The Role of Small Proteins in Cyanobacterial Stress Responses.Bioessays. 2025 Mar;47(3):e202400245. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400245. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39668401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

