Antibody titres decline 3-month post-vaccination with BNT162b2
- PMID: 34232116
- PMCID: PMC8300930
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1953403
Antibody titres decline 3-month post-vaccination with BNT162b2
Abstract
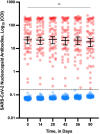
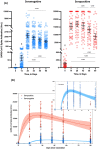
Several studies reported on the humoral response in subjects having received the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. However, data on the kinetics of antibodies 3 months post-vaccination are currently lacking and are important to drive the future vaccination strategy. The CRO-VAX HCP study is an ongoing multicentre, prospective and interventional study designed to assess the antibody response in a population of healthcare professionals who had received two doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Two hundred individuals underwent a blood drawn within 2 days before the first vaccine dose. One-hundred and forty-two persons (71%) were categorized as seronegative at baseline while 58 (29%) were seropositive. Samples were then collected after 14, 28, 42, 56, and 90 days. Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and the receptor binding domain of the S1 subunit of the spike protein were measured in all individuals at different time points. Using a one-compartment kinetics model, the time to maximum concentration was estimated at 36 ± 3 days after the first dose and the estimated half-life of antibodies was 55 days (95% CI: 37-107 days) in seronegative participants. In seropositive participants, the time to maximum concentration was estimated at 24 ± 4 days and the estimated half-life was 80 days (95% CI: 46-303 days). The antibody response was higher in seropositive compared to seronegative participants. In both seropositive and seronegative subjects, a significant antibody decline was observed at 3 months compared to the peak response. Nevertheless, the humoral response remained robust in all participants.
Keywords: BNT162b2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody response; mRNA vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
