Perinatal transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and transfer of maternal IgG/neutralizing anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from mothers with asymptomatic infection during pregnancy
- PMID: 34232457
- PMCID: PMC8262126
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-021-01650-5
Perinatal transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and transfer of maternal IgG/neutralizing anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from mothers with asymptomatic infection during pregnancy
Abstract
Purpose: COVID-19 pandemic remains a serious public health threat worldwide. In view of the limited data on the risk of perinatal transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and transfer of maternal anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, the present study was undertaken.
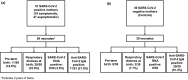
Methods: A prospective study including 57 pregnant women with a positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA test (SARS-CoV-2-RNA+) and 59 neonates born to them was conducted at Pune, India. 39 viral RNA negative (SARS-CoV-2-RNA-negative) pregnant women and their 39 neonates were included as controls. Neonatal nasal swab/cord blood samples were subjected to SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection by RT-PCR for investigation of perinatal transmission. Transfer of maternal antibodies was studied using ELISA and PRNT.
Results: 10/57 SARS-CoV-2-RNA+ mothers were symptomatic. The duration between COVID-19 diagnosis and delivery was ≤ 7 days for 82.4%. Perinatal transmission as evidenced by viral RNA in the neonatal nasal swab/cord blood (CB) was 3.6%. IgG-anti-SARS-CoV-2 positivity was 21.6%. Of the 39 neonates born to SARS-CoV-2-RNA-negative mothers, 20 (51%) and none, respectively, were positive for IgG-anti-SARS-CoV-2 and viral RNA. Preterm deliveries were higher in SARS-CoV-2-RNA+ (18.6%) than SARS-CoV-2 RNA-negative (0/39) mothers (p < 0.005). Respiratory distress at birth (< 4 h) was higher among neonates of SARS-CoV-2-RNA+ (20/59, 33.9%) than SARS-CoV-2-RNA-negative mothers (3/39, 7.7%; p < 0.001). ~ 75% IgG-positives exhibited neutralization potential with mean PRNT titers of 42.4 ± 24 (SARS-CoV-2-RNA+) and 72.3 ± 46.7 (SARS-CoV-2 RNA-negative); higher in the latter (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The rate of perinatal transmission was low. Transfer of maternal antibodies was lower among SARS-CoV-2-RNA+ mothers than SARS-CoV-2-RNA-negative mothers with subclinical infection during pregnancy. Presence of neutralizing antibodies in majority of IgG-positives suggests protection from SARS-CoV-2 in early life.
Keywords: COVID-19; India; Neutralizing antibodies; Perinatal transmission; Pregnant women; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Neonates Born to Mothers With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) - National Neonatology Forum (NNF) India COVID-19 Registry.Indian Pediatr. 2021 Jun 15;58(6):525-531. doi: 10.1007/s13312-021-2234-2. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Indian Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33742609 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between viral load, infection-to-delivery interval and mother-to-child transfer of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jun;57(6):974-978. doi: 10.1002/uog.23639. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33798280 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Maternal and Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load, Transplacental Antibody Transfer, and Placental Pathology in Pregnancies During the COVID-19 Pandemic.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 1;3(12):e2030455. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.30455. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33351086 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection, its Vertical Transmission, and Impact on Overall Perinatal Outcomes: A Narrative Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2022;18(2):103-109. doi: 10.2174/1573396317666211124095020. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2022. PMID: 34819008 Review.
-
Rates of Maternal and Perinatal Mortality and Vertical Transmission in Pregnancies Complicated by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-Co-V-2) Infection: A Systematic Review.Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Aug;136(2):303-312. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004010. Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32516273
Cited by
-
Preliminary results on transmission of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies to the fetus and serum neutralizing activity.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022 Aug;158(2):476-478. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14185. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 35315934 Free PMC article.
-
Transplacental Transfer of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain IgG Antibodies from Mothers to Neonates in a Cohort of Pakistani Unvaccinated Mothers.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 6;11(6):1651. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061651. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371746 Free PMC article.
-
Immune profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy reveals NK cell and γδ T cell perturbations.JCI Insight. 2023 Apr 10;8(7):e167157. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.167157. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37036008 Free PMC article.
-
A large series of molecular and serological specimens to evaluate mother-to-child SARS-CoV-2 transmission: a prospective study from the Italian Obstetric Surveillance System.Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Jan;126:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.10.045. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36368605 Free PMC article.
-
Cord Blood SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies and Their Association With Maternal Immunity and Neonatal Outcomes.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jun 29;10:883185. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.883185. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35844759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, Qi X, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Tong S. Epidemiology of COVID-19 among children in China. Pediatics. 2020;145:e20200702. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous