Verticillium dahliae secreted protein Vd424Y is required for full virulence, targets the nucleus of plant cells, and induces cell death
- PMID: 34233072
- PMCID: PMC8358993
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13100
Verticillium dahliae secreted protein Vd424Y is required for full virulence, targets the nucleus of plant cells, and induces cell death
Abstract
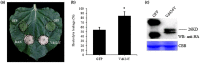
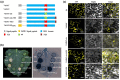
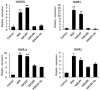
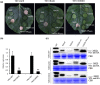
Fungal pathogens secrete effector proteins that regulate host immunity and can suppress basal defence mechanisms against colonization in plants. Verticillium dahliae is a widespread and destructive soilborne fungus that can cause vascular wilt disease and reduces plant yields. However, little is currently known about how the effectors secreted by V. dahliae function. In this study, we analysed and identified 34 candidate effectors in the V. dahliae secretome and found that Vd424Y, a glycoside hydrolase family 11 protein, was highly upregulated during the early stages of V. dahliae infection in cotton plants. This protein was located in the nucleus and its deletion compromised the virulence of the fungus. The transient expression of Vd424Y in Nicotiana benthamiana induced BAK1- and SOBIR1-dependent cell death and activated both salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signalling. This enhanced its resistance to the oomycetes Phytophthora capsici in a way that depended on its nuclear localization signal and signal peptides. Our results demonstrate that Vd424Y is an important effector protein targeting the host nucleus to regulate and activate effector-triggered immunity in plants.
Keywords: Verticillium dahliae; cell death; effector; nuclear localization signal; virulence.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Suppression of plant immunity by Verticillium dahliae effector Vd6317 through AtNAC53 association.Plant J. 2024 Aug;119(4):1767-1781. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16883. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 38924284
-
The Verticillium-specific protein VdSCP7 localizes to the plant nucleus and modulates immunity to fungal infections.New Phytol. 2017 Jul;215(1):368-381. doi: 10.1111/nph.14537. Epub 2017 Apr 13. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 28407259
-
Verticillium dahliae Effector VdCE11 Contributes to Virulence by Promoting Accumulation and Activity of the Aspartic Protease GhAP1 from Cotton.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0354722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03547-22. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36656049 Free PMC article.
-
Insights to Gossypium defense response against Verticillium dahliae: the Cotton Cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 May 1;23(2):142. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01065-5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37121989 Review.
-
The secretome of Verticillium dahliae in collusion with plant defence responses modulates Verticillium wilt symptoms.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Oct;97(5):1810-1822. doi: 10.1111/brv.12863. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 35478378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The secreted FoAPY1 peptidase promotes Fusarium oxysporum invasion.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1040302. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1040302. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338032 Free PMC article.
-
The Secreted Ribonuclease SRE1 Contributes to Setosphaeria turcica Virulence and Activates Plant Immunity.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 8;13:941991. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.941991. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35875548 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Characterization of the Secretome of the Fungal Pathogen Thielaviopsis punctulata, the Causal Agent of Date Palm Black Scorch Disease.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;9(3):303. doi: 10.3390/jof9030303. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983471 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization sequence of MoHTR1, a Magnaporthe oryzae effector, for transcriptional reprogramming of immunity genes in rice.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 11;15(1):9764. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54272-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39528565 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Functional Analysis of a Novel Hydrophobic Protein VdHP1 from Verticillium dahliae.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0247821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02478-21. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35377232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., Uematsu, S. & Takeuchi, O. (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell, 124 783–801. - PubMed
-
- Asai, S. & Yoshioka, H. (2009) Nitric oxide as a partner of reactive oxygen species participates in disease resistance to necrotrophic pathogen Botrytis cinerea in Nicotiana benthamiana . Molecular Plant‐Microbe Interactions, 22 619–629. - PubMed
-
- Chisholm, S.T., Coaker, G., Day, B. & Staskawicz, B.J. (2006) Host–microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell, 124 803–814. - PubMed
-
- Dean, J., Goodwin, P. & Hsiang, T. (2005) Induction of glutathione S‐transferase genes of Nicotiana benthamiana following infection by Colletotrichum destructivum and C. orbiculare and involvement of one in resistance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- Dingwall, C. & Laskey, R.A. (1991) Nuclear targeting sequences—a consensus? Trends in Biochemical Science, 16, 478–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

