Infection and Vaccine-Induced Neutralizing-Antibody Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 Variants
- PMID: 34233096
- PMCID: PMC8279090
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2107799
Infection and Vaccine-Induced Neutralizing-Antibody Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 Variants
Figures
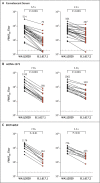
Update of
-
Infection and vaccine-induced neutralizing antibody responses to the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.1 variant.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 10:2021.05.09.443299. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.09.443299. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 12;385(7):664-666. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2107799. PMID: 34013272 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1U54CA260563/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- U19 AI057266/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93021C00016/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P51 OD011132/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA260563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201400004C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 3U19AI057266-17S1/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural funding from the National Institute of/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- NIH P51 OD011132/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
