Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile
- PMID: 34233097
- PMCID: PMC8279092
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107715
Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile
Abstract
Background: Mass vaccination campaigns to prevent coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) are occurring in many countries; estimates of vaccine effectiveness are urgently needed to support decision making. A countrywide mass vaccination campaign with the use of an inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine (CoronaVac) was conducted in Chile starting on February 2, 2021.
Methods: We used a prospective national cohort, including participants 16 years of age or older who were affiliated with the public national health care system, to assess the effectiveness of the inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine with regard to preventing Covid-19 and related hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and death. We estimated hazard ratios using the extension of the Cox proportional-hazards model, accounting for time-varying vaccination status. We estimated the change in the hazard ratio associated with partial immunization (≥14 days after receipt of the first dose and before receipt of the second dose) and full immunization (≥14 days after receipt of the second dose). Vaccine effectiveness was estimated with adjustment for individual demographic and clinical characteristics.
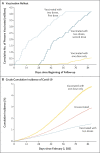
Results: The study was conducted from February 2 through May 1, 2021, and the cohort included approximately 10.2 million persons. Among persons who were fully immunized, the adjusted vaccine effectiveness was 65.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 65.2 to 66.6) for the prevention of Covid-19 and 87.5% (95% CI, 86.7 to 88.2) for the prevention of hospitalization, 90.3% (95% CI, 89.1 to 91.4) for the prevention of ICU admission, and 86.3% (95% CI, 84.5 to 87.9) for the prevention of Covid-19-related death.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectively prevented Covid-19, including severe disease and death, a finding that is consistent with results of phase 2 trials of the vaccine. (Funded by Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo and others.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 30;385(14):1336-1337. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112423. Epub 2021 Sep 15. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34525278 No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 30;385(14):1337-1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112423. Epub 2021 Sep 15. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34525279 No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 30;385(14):1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112423. Epub 2021 Sep 15. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34525280 No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 30;385(14):1338-1339. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2112423. Epub 2021 Sep 15. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34525281 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA 2020;324:782-793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
