Individual-specific functional epigenomics reveals genetic determinants of adverse metabolic effects of glucocorticoids
- PMID: 34233159
- PMCID: PMC8340270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.06.004
Individual-specific functional epigenomics reveals genetic determinants of adverse metabolic effects of glucocorticoids
Abstract
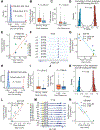
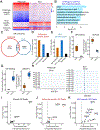
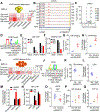
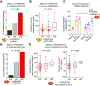
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are widely used as anti-inflammatory drugs, but their long-term use has severe metabolic side effects. Here, by treating multiple individual adipose stem cell-derived adipocytes and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes with the potent GC dexamethasone (Dex), we uncovered cell-type-specific and individual-specific GC-dependent transcriptomes and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) cistromes. Individual-specific GR binding could be traced to single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that altered the binding motifs of GR or its cooperating factors. We also discovered another set of genetic variants that modulated Dex response through affecting chromatin accessibility or chromatin architecture. Several SNPs that altered Dex-regulated GR binding and gene expression controlled Dex-driven metabolic perturbations. Remarkably, these genetic variations were highly associated with increases in serum glucose, lipids, and body mass in subjects on GC therapy. Knowledge of the genetic variants that predispose individuals to metabolic side effects allows for a precision medicine approach to the use of clinically relevant GCs.
Keywords: adipocyte; gene regulation; genetic variation; glucocorticoid receptor; hepatocyte; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.A.L. is an advisory board member for Pfizer and consultant to Flare Therapeutics, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis. M.V.R. receives investigator-initiated research support from Servier. D.J.R. is an advisory board member for Alnylam, Novartis, Pfizer, and Verve and a co-founder of Staten Biotechnology. C.H.-P. is an advisory board member for Adaptive Biotechnology, is on the Data Monitoring Committee for Novartis, and has received honorarium from Amgen and Erytech. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Genetic variation predicts glucocorticoid action.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Oct;17(10):576. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00544-8. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34326525 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bachmann PS, Gorman R, Papa RA, Bardell JE, Ford J, Kees UR, Marshall GM, and Lock RB (2007). Divergent mechanisms of glucocorticoid resistance in experimental models of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 67, 4482–4490. - PubMed
-
- Brotman DJ, Girod JP, Garcia MJ, Patel JV, Gupta M, Posch A, Saunders S, Lip GY, Worley S, and Reddy S. (2005). Effects of short-term glucocorticoids on cardiovascular biomarkers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90, 3202–3208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

