Sphingolipids in metabolic disease: The good, the bad, and the unknown
- PMID: 34233172
- PMCID: PMC8269961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.06.006
Sphingolipids in metabolic disease: The good, the bad, and the unknown
Abstract
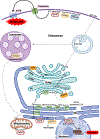
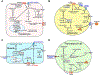
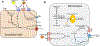
The bioactive sphingolipid metabolites ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) are a recent addition to the lipids accumulated in obesity and have emerged as important molecular players in metabolic diseases. Here we summarize evidence that dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism correlates with pathogenesis of metabolic diseases in humans. This review discusses the current understanding of how ceramide regulates signaling and metabolic pathways to exacerbate metabolic diseases and the Janus faces for its further metabolite S1P, the kinases that produce it, and the multifaceted and at times opposing actions of S1P receptors in various tissues. Gaps and limitations in current knowledge are highlighted together with the need to further decipher the full array of their actions in tissue dysfunction underlying metabolic pathologies, pointing out prospects to move this young field of research toward the development of effective therapeutics.
Keywords: Ceramide; metabolic diseases; sphingolipid metabolites; sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids: players in the pathology of metabolic disease.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jan;20(1):34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Nov 13. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19008117 Review.
-
Sphingolipids, insulin resistance, and metabolic disease: new insights from in vivo manipulation of sphingolipid metabolism.Endocr Rev. 2008 Jun;29(4):381-402. doi: 10.1210/er.2007-0025. Epub 2008 May 1. Endocr Rev. 2008. PMID: 18451260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolism and intestinal tumorigenesis: lipid signaling strikes again.Cell Cycle. 2007 Mar 1;6(5):522-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.5.3903. Epub 2007 Mar 21. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17361098 Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a key metabolite linking sphingolipids to glycerophospholipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1841(5):766-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23994042 Review.
-
ORMDL in metabolic health and disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 May;245:108401. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108401. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37003301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sphingosine kinase 1 contributes to the metastatic potential of epithelial ovarian cancer to the adipocyte-rich niche.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022 Nov 16;11(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00358-y. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36384540 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics-based study of the effect of dietary N-carbamoylglutamic acid addition to heifers in late pregnancy on newborn calves.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Feb 12;11:1335897. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1335897. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38410738 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 (NSM2) in the Control of Neutral Lipid Storage in T Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 13;25(6):3247. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063247. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542220 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements on the Multifaceted Roles of Sphingolipids in Hematological Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 22;23(21):12745. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112745. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taurocholic acid promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via S1PR2/p38 MAPK/YAP signaling under cholestatic conditions.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Apr;29(2):465-481. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0327. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36800698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Fadel F, Fayyaz S, Japtok L, and Kleuser B (2016). Involvement of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in Palmitate-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Physiol. Biochem 40, 1637–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

