Association between copeptin levels and treatment responses to hypertonic saline infusion in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34233437
- PMCID: PMC8476303
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.20.233
Association between copeptin levels and treatment responses to hypertonic saline infusion in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Copeptin is secreted in equimolar amounts as arginine vasopressin, main hormone regulating body fluid homeostasis. A recent study reported a copeptin-based classification of osmoregulatory defects in syndromes of inappropriate antidiuresis that may aid in prediction of therapeutic success. We investigated usefulness of copeptin for differentiating etiologies of hyponatremia and predicting efficacy and safety of hypertonic saline treatment in hyponatremic patients.
Methods: We performed a multicenter, prospective cohort study of 100 inpatients with symptomatic hyponatremia (corrected serum sodium [sNa] ≤ 125 mmol/L) treated with hypertonic saline. Copeptin levels were measured at baseline and 24 hours after treatment initiation, and patients were classified as being below or above median of copeptin at baseline or at 24 hours, respectively. Correlations between target, under correction, and overcorrection rates of sNa within 24 hours/24-48 hours and copeptin levels at baseline/24 hours were analyzed.
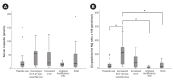
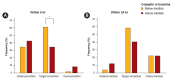
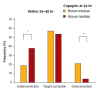
Results: Mean sNa and median copeptin levels were 117.9 and 16.9 pmol/L, respectively. Ratio of copeptin-to-urine sodium allowed for an improved differentiation among some (insufficient effective circulatory volume), but not all hyponatremia etiologic subgroups. Patients with below-median copeptin levels at baseline achieved a higher target correction rate in 6/24 hours (odds ratio [OR], 2.97; p = 0.02/OR, 6.21; p = 0.006). Patients with below-median copeptin levels 24 hours after treatment showed a higher overcorrection rate in next 24 hours (OR, 18.00, p = 0.02).
Conclusion: There is a limited diagnostic utility of copeptin for differential diagnosis of hyponatremia. However, copeptin might be useful for predicting responses to hypertonic saline treatment in hyponatremic patients.
Keywords: Copeptins; Diagnosis; Hypertonic saline solution; Hyponatremia; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk of Overcorrection in Rapid Intermittent Bolus vs Slow Continuous Infusion Therapies of Hypertonic Saline for Patients With Symptomatic Hyponatremia: The SALSA Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Jan 1;181(1):81-92. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.5519. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33104189 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Copeptin in the differential diagnosis of hyponatremia.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jan;94(1):123-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1426. Epub 2008 Nov 4. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 18984663
-
An abnormal apelin/vasopressin balance may contribute to water retention in patients with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) and heart failure.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 May;98(5):2084-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3794. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23515451
-
Copeptin and its role in the diagnosis of diabetes insipidus and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019 Jul;91(1):22-32. doi: 10.1111/cen.13991. Epub 2019 May 8. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 31004513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of symptomatic hyponatremia.Am J Med Sci. 2003 Jul;326(1):25-30. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200307000-00004. Am J Med Sci. 2003. PMID: 12861122 Review.
Cited by
-
Korean Society of Nephrology 2022 Recommendations on Controversial Issues in Diagnosis and Management of Hyponatremia.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2022 Jun;20(1):21-38. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2022.20.1.21. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2022. PMID: 36451712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation and management of hypernatremia in adults: clinical perspectives.Korean J Intern Med. 2023 May;38(3):290-302. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.346. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Korean J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36578134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Utility of Copeptin Measurement in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Secretion.Horm Res Paediatr. 2025 Jun 21:1-10. doi: 10.1159/000547012. Online ahead of print. Horm Res Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 40544834 Free PMC article.
-
Review novel insights into the diagnostic and prognostic function of copeptin in daily clinical practice.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3755-3765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08246-2. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. Retraction in: Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Aug;50(8):7143. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08615-x. PMID: 36662451 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Korean Society of Nephrology 2022 Recommendations on controversial issues in diagnosis and management of hyponatremia.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2022 Jul;41(4):393-411. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.33.555. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35919925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spasovski G, Vanholder R, Allolio B, et al. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014;170:G1–G47. - PubMed
-
- Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1581–1589. - PubMed
-
- Gross P, Reimann D, Neidel J, et al. The treatment of severe hyponatremia. Kidney Int Suppl. 1998;64:S6–S11. - PubMed
-
- Sterns RH, Riggs JE, Schochet SS., Jr Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1535–1542. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

