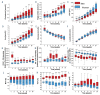
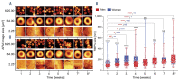
Sex-dependent membranopathy in stored human red blood cells
- PMID: 34233452
- PMCID: PMC8485678
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278895
Sex-dependent membranopathy in stored human red blood cells
Figures

Similar articles
-
PRESERVATION OF RED CELLS: OBSERVATIONS ON CERTAIN METABOLIC CHANGES IN STORED BLOOD.Bull Calcutta Sch Trop Med. 1965 Jan;13:7-8. Bull Calcutta Sch Trop Med. 1965. PMID: 14281064 No abstract available.
-
[USE OF WHOLE AND PRESERVED WHOLE BLOOD AND OF STORED RED CELLS].Sangre (Barc). 1963;18:299-304. Sangre (Barc). 1963. PMID: 14118432 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
[THE USE OF FRESH BLOOD, STORED WHOLE BLOOD AND OF CONCENTRATED RED BLOOD CELLS. PROBLEMS POSED BY THE PREPARATION OF RED BLOOD CELL CONCENTRATES FOR TRANSFUSION USES].Sangre (Barc). 1963;42:259-64. Sangre (Barc). 1963. PMID: 14112674 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Chronological storage age and metabolic age of stored red blood cells: are they the same?Transfusion. 2019 May;59(5):1620-1623. doi: 10.1111/trf.15248. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Transfusion. 2019. PMID: 30865302 Review.
-
Stored red blood cells: a changing universe waiting for its map(s).J Proteomics. 2010 Jan 3;73(3):374-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2009.11.001. Epub 2009 Nov 25. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 19931659 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of storage duration on outcome of patients receiving red blood cell in emergency department.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 8;14(1):23463. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74114-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39379435 Free PMC article.
-
Biopreservation and Reversal of Oxidative Injury During Blood Storage by a Novel Curcumin-based Gel Formulation.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:rs.3.rs-4277591. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4277591/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82943-1. PMID: 38766242 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Red Blood Cell Donor Sex Associated Effects on Morbidity and Mortality in the Extremely Preterm Newborn.Children (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;9(12):1980. doi: 10.3390/children9121980. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-Specific Differences of Adenosine Triphosphate Levels in Red Blood Cells Isolated From ApoE/LDLR Double-Deficient Mice.Front Physiol. 2022 Feb 18;13:839323. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.839323. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35250640 Free PMC article.
-
Biopreservation and reversal of oxidative injury during blood storage by a novel curcumin-based gel formulation.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82943-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39733159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szczesny-Malysiak E, Dybas J, Blat A, et al. . Irreversible alterations in the hemoglobin structure affect oxygen binding in human packed red blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020; 1867(11):118803. - PubMed
-
- Tzounakas VL, Georgatzakou HT, Kriebardis AG, et al. . Donor variation effect on red blood cell storage lesion: a multivariable, yet consistent, story. Transfusion 2016;56(6):1274-1286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

