Multicenter randomized controlled trial and registry study to assess the safety and efficacy of the NanoKnife® system for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: overview of study protocols
- PMID: 34233640
- PMCID: PMC8261981
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08474-4
Multicenter randomized controlled trial and registry study to assess the safety and efficacy of the NanoKnife® system for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: overview of study protocols
Abstract
Background: Irreversible electroporation (IRE) is a local ablation technique utilizing high voltage, low energy direct current to create nanopores in cell membrane which disrupt homeostasis and leads to cell death. Previous reports have suggested IRE may have a role in treating borderline resectable and unresectable Stage 3 pancreatic tumors.
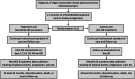
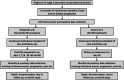
Methods: Patients with Stage 3 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) will be enrolled in either a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial (RCT) or a multicenter registry study. Subjects enrolled in the RCT must have no evidence of disease progression after 3 months of modified FOLFIRINOX (mFOLFIRINOX) treatment prior to being randomization to either a control or IRE arm. Post-induction and post-IRE treatment for the control and IRE arms, respectively, will be left to the discretion of the treating physician. The RCT will enroll 528 subjects with 264 per arm and include up to 15 sites. All subjects will be followed for at least 24 months or until death. The registry study will include two cohorts of patients with Stage 3 PDAC, patients who received institutional standard of care (SOC) alone and those treated with IRE in addition to SOC. Both cohorts will be required to have undergone at least 3 months of SOC without progression prior to enrollment. The registry study will enroll 532 patients with 266 patients in each arm. All patients will be followed for at least 24 months or until death. The primary efficacy endpoint for both studies will be overall survival (OS). Co-primary safety endpoints will be 1) time from randomization or enrollment in the registry to death or new onset of Grade 4 adverse event (AE), and (2 high-grade complications defined as any AE or serious AE (SAE) with a CTCAE v5.0 grade of 3 or higher. Secondary endpoints will include progression-free survival, cancer-related pain, quality of life, and procedure-related pain for the IRE arm only.
Discussion: These studies are intended to provide Level 1 clinical evidence and real-world data demonstrating the clinical utility and safety of the use of IRE in combination with chemotherapy in patients with Stage 3 PDAC.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT03899636 and NCT03899649. Registered April 2, 2019. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) trial G180278 approved on May 3, 2019.
Keywords: Ablation; Irreversible electroporation; Locally advanced pancreatic cancer; Modified FOLFIRINOX; NanoKnife system; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
AngioDynamics (Latham, New York) provided funding to OMI1 for the power analyses and the development of the statistical analysis plan presented in the present paper. ZS and KM are employees of OM1, Inc. RCGM is a paid educational consultant to AngioDynamics. GN, MMB, and PJH have received consulting fees from AngioDynamics and their institutions are receiving research support from AngioDynamics for the ongoing studies described in the present work.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. CancerStat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html. Accessed 6 Jan 2020.
-
- van Roessel S, Kasumova GG, Verheij J, Najarian RM, Maggino L, de Pastena M, Malleo G, Marchegiani G, Salvia R, Ng SC, de Geus SW, Lof S, Giovinazzo F, van Dam JL, Kent TS, Busch OR, van Eijck CH, Koerkamp BG, Abu Hilal M, Bassi C, Tseng JF, Besselink MG. International validation of the eighth edition of the American joint committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system in patients with resected pancreatic cancer. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(12):e183617. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.3617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Loehrer PJ, Sr, Feng Y, Cardenes H, Wagner L, Brell JM, Cella D, Flynn P, Ramanathan RK, Crane CH, Alberts SR, Benson AB., III Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: an eastern cooperative oncology group trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(31):4105–4112. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Kuk D, Castillo CF, Basturk O, Wolfgang CL, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Ferrone CR, Morales-Oyarvide V, He J, Weiss MJ, Hruban RH, Gönen M, Klimstra DS, Mino-Kenudson M. Multi-institutional validation study of the American joint commission on Cancer (8th edition) changes for T and N staging in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2017;265(1):185–191. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001763. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Péré-Vergé D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1817–1825. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011923. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous