Common and mutation specific phenotypes of KRAS and BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer cells revealed by integrative -omics analysis
- PMID: 34233735
- PMCID: PMC8265010
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02025-2
Common and mutation specific phenotypes of KRAS and BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer cells revealed by integrative -omics analysis
Abstract
Background: Genes in the Ras pathway have somatic mutations in at least 60 % of colorectal cancers. Despite activating the same pathway, the BRAF V600E mutation and the prevalent mutations in codon 12 and 13 of KRAS have all been linked to different clinical outcomes, but the molecular mechanisms behind these differences largely remain to be clarified.
Methods: To characterize the similarities and differences between common activating KRAS mutations and between KRAS and BRAF mutations, we used genome editing to engineer KRAS G12C/D/V and G13D mutations in colorectal cancer cells that had their mutant BRAF V600E allele removed and subjected them to transcriptome sequencing, global proteomics and metabolomics analyses.
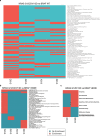
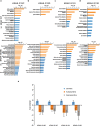
Results: By intersecting differentially expressed genes, proteins and metabolites, we uncovered (i) two-fold more regulated genes and proteins when comparing KRAS to BRAF mutant cells to those lacking Ras pathway mutation, (ii) five differentially expressed proteins in KRAS mutants compared to cells lacking Ras pathway mutation (IFI16, S100A10, CD44, GLRX and AHNAK2) and 6 (CRABP2, FLNA, NXN, LCP1, S100A10 and S100A2) compared to BRAF mutant cells, (iii) 19 proteins expressed differentially in a KRAS mutation specific manner versus BRAF V600E cells, (iv) regulation of the Integrin Linked Kinase pathway by KRAS but not BRAF mutation, (v) regulation of amino acid metabolism, particularly of the tyrosine, histidine, arginine and proline pathways, the urea cycle and purine metabolism by Ras pathway mutations, (vi) increased free carnitine in KRAS and BRAF mutant RKO cells.
Conclusions: This comprehensive integrative -omics analysis confirms known and adds novel genes, proteins and metabolic pathways regulated by mutant KRAS and BRAF signaling in colorectal cancer. The results from the new model systems presented here can inform future development of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches targeting tumors with KRAS and BRAF mutations.
Keywords: BRAF; Colorectal cancer; Integrative -omics analysis; Isogenic cell models; KRAS; Ras pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Concomitant mutations and splice variants in KRAS and BRAF demonstrate complex perturbation of the Ras/Raf signalling pathway in advanced colorectal cancer.Gut. 2009 Sep;58(9):1234-41. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.159137. Epub 2009 May 26. Gut. 2009. PMID: 19474002
-
Relationships among KRAS mutation status, expression of RAS pathway signaling molecules, and clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 21;25(7):808-823. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.808. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30809081 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and prognostic features of patients with detailed RAS/BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer in Japan.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 7;21(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08271-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33962575 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of KRAS and BRAF in stage I-III colorectal cancer. A systematic review.Ann Ital Chir. 2019;90:127-137. Ann Ital Chir. 2019. PMID: 30739887
-
Immunohistochemistry with Anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody is a Sensitive Method for Detection of the BRAF V600E Mutation in Colon Cancer: Evaluation of 120 Cases with and without KRAS Mutation and Literature Review.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jan;25(1):349-359. doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0344-x. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 29127628 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein expression of S100A2 reveals it association with patient prognosis and immune infiltration profile in colorectal cancer.J Cancer. 2023 Jun 19;14(10):1837-1847. doi: 10.7150/jca.83910. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37476187 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Modulation of PAR-2-Driven Inflammatory Pathways by Oleocanthal: Attenuation of TNF-α and Calcium Dysregulation in Colorectal Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 24;26(7):2934. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072934. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243559 Free PMC article.
-
The ANXA2/S100A10 Complex-Regulation of the Oncogenic Plasminogen Receptor.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 26;11(12):1772. doi: 10.3390/biom11121772. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylated Colorectal Cancer Tumours Present a Myc-Driven Hypermetabolism with a One-Carbon Signature Associated with Worsen Prognosis.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 6;12(3):590. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030590. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540202 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated model for predicting KRAS dependency.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 May 4;19(5):e1011095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011095. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37141389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Roock W, Jonker DJ, Di Nicolantonio F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Tu D, Siena S, Lamba S, Arena S, Frattini M, Piessevaux H, et al. Association of KRAS p.G13D mutation with outcome in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. JAMA. 2010;304:1812–20. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1535. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

