Thymoquinone Preserves Pancreatic Islets Structure Through Upregulation of Pancreatic β-Catenin in Hypothyroid Rats
- PMID: 34234489
- PMCID: PMC8254558
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S317417
Thymoquinone Preserves Pancreatic Islets Structure Through Upregulation of Pancreatic β-Catenin in Hypothyroid Rats
Abstract
Background: Altered status of thyroid hormones, which have a key role in regulating metabolism, was reported to affect glucose homeostasis and insulin secretion.
Objective: This study was designed to assess the impact of propylthiouracil (PTU)-induced hypothyroidism on the pancreatic islet cells and the efficacy of thymoquinone (TQ) in alleviating this impact and explore the mechanism behind it alleviating oxidative stress and affecting β-catenin expression.
Materials and methods: PTU (6 mg/kg/body weight) was used to induce hypothyroidism in Wistar rats. Four groups of rats (n=6 each) were utilized in this study. Untreated hypothyroid and TQ-treated hypothyroid groups (50 mg/kg/body weight for 4 weeks) were included. Thyroid functions, antioxidant profile and pancreatic β-catenin and IL-10 mRNA were measured. Histopathological and immunohistochemical assessment of the pancreas was performed.
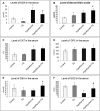
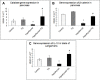
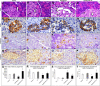
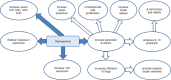
Results: PTU administration induced a hypothyroid status that was associated with a marked disturbed oxidant/antioxidant status and a significant hyperglycemia (p<0:001), hypoinsulinemia (p=0.01) and decreased HOMA-β-cell (p<0.001). Islet cells of hypothyroid pancreas showed many degenerative changes with increased apoptosis, reduced insulin β-catenin immunoexpression. Administration of TQ alleviated these effects on the thyroid function, antioxidants, structure of pancreatic islet cells. Up-regulation of β-catenin, IL-10 and CAT gene expression in pancreatic islets after treatment with TQ supported its antioxidant and preserving β-cell function and viability mechanistic action.
Conclusion: TQ alleviated PTU-induced hypothyroidism changes in insulin homeostasis and pancreatic β cells mostly through its antioxidant effect as well as up-regulation of pancreatic β-catenin expression.
Keywords: Nigella sativa; caspase-3; glucose; hypothyroidism; insulin; pancreas.
© 2021 Faddladdeen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thymoquinone protects the testes of hypothyroid rats by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress and promoting SIRT1 testicular expression.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 24;13:1040857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1040857. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36506574 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone reverses nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) associated with experimental hypothyroidism.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2019;60(2):479-486. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2019. PMID: 31658321
-
Thymoquinone Upregulates Catalase Gene Expression and Preserves the Structure of the Renal Cortex of Propylthiouracil-Induced Hypothyroid Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jul 20;2020:3295831. doi: 10.1155/2020/3295831. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32774669 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of oxidative stress, suppression of glucose-induced insulin release, ATP production, glucokinase activity, and histomorphometric changes in pancreatic islets of hypothyroid rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;791:147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.08.024. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27568837
-
Thymoquinone Ameliorate Hepatorenal Toxicity Associated With Propylthiouracil-Induced Hypothyroidism in Juvenile Rats.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2021 Oct-Dec;17(4):432-439. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2021.432. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2021. PMID: 35747868 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interplay between Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Fetuin-A, Retinol Binding Protein 4 and Thyroid Function in Metabolic Dysregulation.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 29;12(4):300. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040300. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35448487 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khurana A, Dhoat P, Jain G. Prevalence of thyroid disorders in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Indian Acad Clin Med. 2016;17:12–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

