An Overview of Similarities and Differences in Metabolic Actions and Effects of Central Nervous System Between Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs) and Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT-2is)
- PMID: 34234493
- PMCID: PMC8254548
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S312527
An Overview of Similarities and Differences in Metabolic Actions and Effects of Central Nervous System Between Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs) and Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT-2is)
Abstract
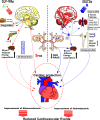
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and SGLT-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2is) are novel antidiabetic medications associated with considerable cardiovascular benefits therapying treatment of diabetic patients. GLP-1 exhibits atherosclerosis resistance, whereas SGLT-2i acts to ameliorate the neuroendocrine state in the patients with chronic heart failure. Despite their distinct modes of action, both factors share pathways by regulating the central nervous system (CNS). While numerous preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that GLP-1 can access various nuclei associated with energy homeostasis and hedonic eating in the CNS via blood-brain barrier (BBB), research on the activity of SGLT-2is remains limited. In our previous studies, we demonstrated that both GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) liraglutide and exenatide, as well as an SGLT-2i, dapagliflozin, could activate various nuclei and pathways in the CNS of Sprague Dawley (SD) rats and C57BL/6 mice, respectively. Moreover, our results revealed similarities and differences in neural pathways, which possibly regulated different metabolic effects of GLP-1RA and SGLT-2i via sympathetic and parasympathetic systems in the CNS, such as feeding, blood glucose regulation and cardiovascular activities (arterial blood pressure and heart rate control). In the present article, we extensively discuss recent preclinical studies on the effects of GLP-1RAs and SGLT-2is on the CNS actions, with the aim of providing a theoretical explanation on their mechanism of action in improvement of the macro-cardiovascular risk and reducing incidence of diabetic complications. Overall, these findings are expected to guide future drug design approaches.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; brain nuclei; cardiovascular diseases; diabetes; diabetic complications; obesity.
© 2021 Wen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

