Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Catabolizing Enzymes Predict Better Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients and Correlates With Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells
- PMID: 34235182
- PMCID: PMC8255376
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.697922
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Catabolizing Enzymes Predict Better Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients and Correlates With Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells
Abstract
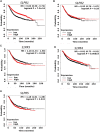
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is associated with a poor prognosis. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a potent sphingolipid metabolite, has been implicated in many processes that are important for breast cancer (BC). S1P signaling regulates tumorigenesis, and response to chemotherapy and immunotherapy by affecting the trafficking, differentiation or effector function of tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs). Objective: In this study, using bioinformatics tools and publicly available databases, we have analyzed the prognostic value of S1P metabolizing genes and their correlation with TIICs in BC patients. Methods: The expression of S1P metabolizing genes and receptors was evaluated by the UALCAN cancer database. The correlation between mRNA expression of S1P metabolizing genes and receptors and survival outcome of breast cancer patients was analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier plotter database. The association between the gene expression and infiltration of immune cells in the tumors was analyzed by "Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER). In silico protein expression analysis was done using the Human Protein Atlas" database. Results: TNBC patients with lower expression of S1P phosphatase 1 (SGPP1) or lipid phosphate phosphatase 3 (PLPP3) have much shorter relapse-free survival than the patients with a higher expression of these genes. SGPP1 and PLPP3 expression show a strong positive correlation with tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells (DCs), CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, neutrophils, and macrophages in the TNBC subtypes. In addition, S1P receptor 4 (S1PR4), an S1P receptor exhibit a strong positive correlation with DCs, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and neutrophils in TNBC. We, therefore, conclude that low expression of SGPP1 and PLPP3 may hinder the recruitment of immune cells to the tumor environment, resulting in the blockage of cancer cell clearance and a subsequent poor prognosis.
Keywords: PLPP3; S1PR4; SGPP1; breast cancer; sphingosine-1-phosphate; tumor-infiltrating immune cells.
Copyright © 2021 Nema and Kumar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Alkabban F. M., Ferguson T. (2020). “Breast Cancer,” in StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing). Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482286/ (Accessed August 20, 2020). - PubMed
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R. L., Torre L. A., Jemal A. (2018). Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clinicians 68, 394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492@10.3322/(ISSN)1542-4863.statistics - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

