Role of Dispersion Interactions in Endohedral TM@(ZnS)12 Structures
- PMID: 34235333
- PMCID: PMC8246693
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02016
Role of Dispersion Interactions in Endohedral TM@(ZnS)12 Structures
Abstract
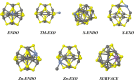
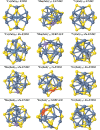
II-VI semiconducting materials are gaining attention due to their optoelectronic properties. Moreover, the addition of transition metals, TMs, might give them magnetic properties. The location and distance of the TM are crucial in determining such magnetic properties. In this work, we focus on small hollow (ZnS)12 nanoclusters doped with TMs. Because (ZnS)12 is a cage-like spheroid, the cavity inside the structure allows for the design of endohedral compounds resembling those of C60. Previous studies theoretically predicted that the first-row TM(ZnS)12 endohedral compounds were thermodynamically unstable compared to the surface compounds, where the TM atom is located at the surface of the cluster. The transition states connecting both structure families were calculated, and the estimated lifetimes of these compounds were predicted to be markedly small. However, in such works dispersion effects were not taken into account. Here, in order to check for the influence of dispersion on the possible stabilization of the desired TM(ZnS)12 endohedrally doped clusters, several functionals are tested and compare to MP2. It is found that the dispersion effects play a very important role in determining the location of the metals, especially in those TMs with the 4s3d shell half-filled or completely filled. In addition, a complete family of TM doped (ZnS)12 nanoclusters is explored using ab initio molecular dynamics simulations and local minima optimizations that could guide the experimental synthesis of such compounds. From the magnetic point of view, the Cr(7S)@(ZnS)12 compound is the most interesting case, since the endohedral isomer is predicted to be the global minimum. Moreover, molecular dynamics simulations show that when the Cr atom is located at the surface of the cluster, it spontaneously migrates toward the center of the cavity at room temperature.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Singh R.; Basu S.; Pal B. Ag+ and Cu2+ Doped CdS Nanorods with Tunable Band Structure and Superior Photocatalytic Activity Under Sunlight. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 279–286. 10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.05.032. - DOI
-
- Horoz S.; Dai Q.; Maloney F. S.; Yakami B.; Pikal J. M.; Zhang X.; Wang J.; Wang W.; Tang J. Absorption Induced by Mn Doping of ZnS for Improved Sensitized Quantum-dot Solar Cells. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 024011–024017. 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.3.024011. - DOI
-
- Rafea M. A.; Farag A. A. M.; Roushdy N. Structural and Optical Characteristics of Nano-Sized Structure of Zn0.5Cd0.5S Thin Films Prepared by Dip-Coating Method. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 485, 660–666. 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.06.048. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

