Skeletal muscle proteomes reveal downregulation of mitochondrial proteins in transition from prediabetes into type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 34235411
- PMCID: PMC8246593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102712
Skeletal muscle proteomes reveal downregulation of mitochondrial proteins in transition from prediabetes into type 2 diabetes
Abstract
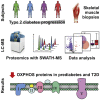
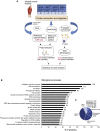
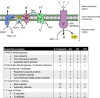
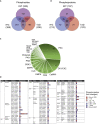
Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is a central defect in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Here, we analyzed skeletal muscle proteome in 148 vastus lateralis muscle biopsies obtained from men covering all glucose tolerance phenotypes: normal, impaired fasting glucose (IFG), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and T2D. Skeletal muscle proteome was analyzed by a sequential window acquisition of all theoretical mass spectra (SWATH-MS) proteomics technique. Our data indicate a downregulation in several proteins involved in mitochondrial electron transport or respiratory chain complex assembly already in IFG and IGT muscles, with most profound decreases observed in T2D. Additional phosphoproteomic analysis reveals altered phosphorylation in several signaling pathways in IFG, IGT, and T2D muscles, including those regulating glucose metabolic processes, and the structure of muscle cells. These data reveal several alterations present in skeletal muscle already in prediabetes and highlight impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism in the trajectory from prediabetes into T2D.
Keywords: Diabetology; Molecular biology; Proteomics.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- American Diabetes Association Improving care and promoting health in populations: standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S7–S12. - PubMed
-
- Batista T.M., Jayavelu A.K., Wewer Albrechtsen N.J., Iovino S., Lebastchi J., Pan H., Dreyfuss J.M., Krook A., Zierath J.R., Mann M., Kahn C.R. A cell-autonomous signature of dysregulated protein phosphorylation underlies muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020;32:844–859.e5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cline G.W., Petersen K.F., Krssak M., Shen J., Hundal R.S., Trajanoski Z., Inzucchi S., Dresner A., Rothman D.L., Shulman G.I. Impaired glucose transport as a cause of decreased insulin-stimulated muscle glycogen synthesis in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;341:240–246. - PubMed
-
- Cox J., Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1367–1372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

