COVID-19 caused hearing loss
- PMID: 34235578
- PMCID: PMC8263317
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-021-06951-x
COVID-19 caused hearing loss
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this cross-sectional study was to determine if there is a potential link between COVID-19 infection and hearing loss.
Methods: The prospective study was conducted in the COVID Hospital Clinical Centre Niš, Serbia. We performed tonal audiometry and used a custom questionnaire and medical histories to determine the incidence of hearing loss in COVID-19 positive patients.
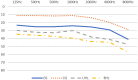
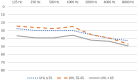
Results: There were 74 patients with COVID-19 that met the inclusion criteria of this study and they composed our experimental group. Fifty-four (73%) were men and 20 (27%) women. There were 30 (40.5%) patients with hearing loss. Seventeen patients had unilateral and 13 had bilateral hearing loss. Significant differences between hearing loss groups and control group were found across all age groups, but not at all frequencies. No important differences were found when unilateral hearing loss and bilateral hearing loss groups were compared. There were no significant differences in distributions of comorbidities between the patients with hearing loss and normal hearing patients.
Conclusions: We found that 30 (40.5%) of the COVID-19 positive patients had sensorineural type of hearing loss. Across all age groups, there were statistically significant differences in frequencies between the COVID-19 positive patients and the control group. There were no significant differences in distributions of comorbidities between the patients with hearing loss and normal hearing patients. Distribution of unilateral and bilateral hearing loss and audiogram types was also not significantly different between the age groups.
Keywords: Audiometry; Covid-19; Hearing loss.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
COVID-19 and its effect on hearing.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Nov;279(11):5473. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07595-1. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35943597 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)—World Health Organization (2020) https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Acessed 18 Oct 2020
-
- Cao Y, Liu X, Xiong L, Cai K (2020) Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS‐CoV‐2: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Med Virol, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7228215/. Acessed 18 Oct 2020 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

