Effect of Sodium Salicylate on Calcium Currents and Exocytosis in Cochlear Inner Hair Cells: Implications for Tinnitus Generation
- PMID: 34235622
- PMCID: PMC8782992
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-021-00747-z
Effect of Sodium Salicylate on Calcium Currents and Exocytosis in Cochlear Inner Hair Cells: Implications for Tinnitus Generation
Abstract
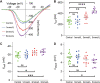
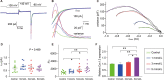
Sodium salicylate is an anti-inflammatory medication with a side-effect of tinnitus. Here, we used mouse cochlear cultures to explore the effects of salicylate treatment on cochlear inner hair cells (IHCs). We found that IHCs showed significant damage after exposure to a high concentration of salicylate. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings showed that 1-5 mmol/L salicylate did not affect the exocytosis of IHCs, indicating that IHCs are not involved in tinnitus generation by enhancing their neuronal input. Instead, salicylate induced a larger peak amplitude, a more negative half-activation voltage, and a steeper slope factor of Ca2+ current. Using noise analysis of Ca2+ tail currents and qRT-PCR, we further found that salicylate increased the number of Ca2+ channels along with CaV1.3 expression. All these changes could act synergistically to enhance the Ca2+ influx into IHCs. Inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ overload significantly attenuated IHC death after 10 mmol/L salicylate treatment. These results implicate a cellular mechanism for tinnitus generation in the peripheral auditory system.
Keywords: CaV1.3 channel; Calcium current; Exocytosis; Inner hair cell; Salicylate; Tinnitus; Whole-cell patch clamp.
© 2021. Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Different CaV1.3 Channel Isoforms Control Distinct Components of the Synaptic Vesicle Cycle in Auditory Inner Hair Cells.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 15;37(11):2960-2975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2374-16.2017. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28193694 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to sodium salicylate disrupts VGLUT3 expression in cochlear inner hair cells and contributes to tinnitus.Physiol Res. 2020 Feb 19;69(1):181-190. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934180. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 31852197 Free PMC article.
-
The Ca2+ channel subunit beta2 regulates Ca2+ channel abundance and function in inner hair cells and is required for hearing.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 26;29(34):10730-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1577-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19710324 Free PMC article.
-
Harmonin enhances voltage-dependent facilitation of Cav1.3 channels and synchronous exocytosis in mouse inner hair cells.J Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;591(13):3253-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.254367. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23613530 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory sensori-neural alterations induced by salicylate.Prog Neurobiol. 2000 Dec;62(6):583-631. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(00)00027-7. Prog Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10880852 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Functional Method of Protector Screening for Zebrafish Lateral Line Hair Cells via the Acoustic Escape Response.Neurosci Bull. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1007/s12264-025-01406-3. Online ahead of print. Neurosci Bull. 2025. PMID: 40329138
-
A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Mar 23;61(4):569. doi: 10.3390/medicina61040569. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40282861 Free PMC article.
-
Acoustic and optoacoustic stimulations in auditory brainstem response test in salicylate induced tinnitus.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11930. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39033-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488197 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium salicylate ameliorates exercise-induced muscle damage in mice by inhibiting NF-kB signaling.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Dec 15;18(1):967. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04433-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 38098039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cazals Y. Auditory sensori-neural alterations induced by salicylate. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;62:583–631. - PubMed
-
- Liu P, Qin D, Huang X, Chen H, Ye W, Lin X, et al. Neurotoxicity of sodium salicylate to the spiral ganglion neurons: GABAA receptor regulates NMDA receptor by Fyn-dependent phosphorylation. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2019;205:469–479. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Zhang H, Li X, Wang Y, Lu H, Qi X, et al. Inhibition of voltage-gated channel currents in rat auditory cortex neurons by salicylate. Neuropharmacology. 2007;53:870–880. - PubMed
-
- Qin DX, Liu PQ, Chen HY, Huang X, Ye WH, Lin XY, et al. Salicylate-induced ototoxicity of spiral ganglion neurons: Ca2+/CaMKII-mediated interaction between NMDA receptor and GABAA receptor. Neurotox Res. 2019;35:838–847. - PubMed
-
- Zugaib J, Ceballos CC, Leão RM. High doses of salicylate reduces glycinergic inhibition in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the rat. Hear Res. 2016;332:188–198. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

