The Castrop formula for calculation of toric intraocular lenses
- PMID: 34236474
- PMCID: PMC8523386
- DOI: 10.1007/s00417-021-05287-w
The Castrop formula for calculation of toric intraocular lenses
Abstract
Purpose: To explain the concept behind the Castrop toric lens (tIOL) power calculation formula and demonstrate its application in clinical examples.
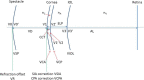
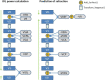
Methods: The Castrop vergence formula is based on a pseudophakic model eye with four refractive surfaces and three formula constants. All four surfaces (spectacle correction, corneal front and back surface, and toric lens implant) are expressed as spherocylindrical vergences. With tomographic data for the corneal front and back surface, these data are considered to define the thick lens model for the cornea exactly. With front surface data only, the back surface is defined from the front surface and a fixed ratio of radii and corneal thickness as preset. Spectacle correction can be predicted with an inverse calculation.
Results: Three clinical examples are presented to show the applicability of this calculation concept. In the 1st example, we derived the tIOL power for a spherocylindrical target refraction and corneal tomography data of corneal front and back surface. In the 2nd example, we calculated the tIOL power with keratometric data from corneal front surface measurements, and considered a surgically induced astigmatism and a correction for the corneal back surface astigmatism. In the 3rd example, we predicted the spherocylindrical power of spectacle refraction after implantation of any toric lens with an inverse calculation.
Conclusions: The Castrop formula for toric lenses is a generalization of the Castrop formula based on spherocylindrical vergences. The application in clinical studies is needed to prove the potential of this new concept.
Keywords: Castrop formula; Gaussian optics; Prediction of postoperative refraction; Toric intraocular lenses; Vergence calculation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

