Automated Vertebral Segmentation and Measurement of Vertebral Compression Ratio Based on Deep Learning in X-Ray Images
- PMID: 34236562
- PMCID: PMC8455797
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-021-00471-0
Automated Vertebral Segmentation and Measurement of Vertebral Compression Ratio Based on Deep Learning in X-Ray Images
Abstract
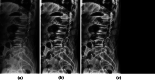
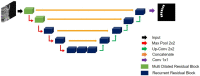
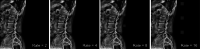
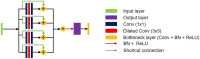
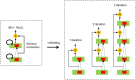
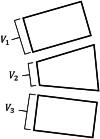
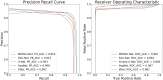
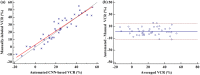
Vertebral compression fracture is a deformity of vertebral bodies found on lateral spine images. To diagnose vertebral compression fracture, accurate measurement of vertebral compression ratio is required. Therefore, rapid and accurate segmentation of vertebra is important for measuring the vertebral compression ratio. In this study, we used 339 data of lateral thoracic and lumbar vertebra images for training and testing a deep learning model for segmentation. The result of segmentation by the model was compared with the manual measurement, which is performed by a specialist. As a result, the average sensitivity of the dataset was 0.937, specificity was 0.995, accuracy was 0.992, and dice similarity coefficient was 0.929, area under the curve of receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.987, and the precision recall curve was 0.916. The result of correlation analysis shows no statistical difference between the manually measured vertebral compression ratio and the vertebral compression ratio using the data segmented by the model in which the correlation coefficient was 0.929. In addition, the Bland-Altman plot shows good equivalence in which VCR values are in the area within average ± 1.96. In conclusion, vertebra segmentation based on deep learning is expected to be helpful for the measurement of vertebral compression ratio.
Keywords: Deep learning; Segmentation; Vertebral compression fracture; Vertebral compression ratio.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Automatic Vertebral Body Segmentation Based on Deep Learning of Dixon Images for Bone Marrow Fat Fraction Quantification.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 2;11:612. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00612. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32982989 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a deep learning model for detecting lumbar vertebral fractures on CT images: An external validation.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Nov;180:111685. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111685. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39197270
-
Automatic detection and segmentation of lumbar vertebrae from X-ray images for compression fracture evaluation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Mar;200:105833. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105833. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33250283
-
A deep learning algorithm for automated measurement of vertebral body compression from X-ray images.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 2;11(1):13732. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93017-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34215761 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning application of vertebral compression fracture detection using mask R-CNN.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 15;14(1):16308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67017-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39009647 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spinopelvic measurements of sagittal balance with deep learning: systematic review and critical evaluation.Eur Spine J. 2022 Aug;31(8):2031-2045. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07155-5. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 35278146
-
Using an Ensemble of Segmentation Methods to Detect Vertebral Bodies on Radiographs.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Oct 3;45(10):1512-1520. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8343. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 39209486
-
NAMSTCD: A Novel Augmented Model for Spinal Cord Segmentation and Tumor Classification Using Deep Nets.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;13(8):1417. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13081417. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37189520 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based quantitative morphological study of anteroposterior digital radiographs of the lumbar spine.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Aug 1;14(8):5385-5395. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-540. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39144021 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of anteroposterior and lateral X-ray based deep learning in the detection of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 18;14(1):28388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79610-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39551876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Y. X. J. Wáng, N. Che-Nordin, M. Deng, J. C. S. Leung, A. W. L. Kwok, L. C. He, J. F. Griffith, T. C. Y. Kwok, P. C. Leung: Osteoporotic vertebral deformity with endplate/cortex fracture is associated with higher further vertebral fracture risk: the Ms. OS (Hong Kong) study results. Osteoporosis International 30(4): 897–905, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Alexandru Daniela, So William. Evaluation and Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Current Geriatrics Reports. 2018;7(4):288–295. doi: 10.1007/s13670-018-0268-7. - DOI
-
- Franklin DB, Hardaway AT, Sheffer BW, Spence DD, Kelly DM, Muhlbauer MS, Warner WC, Sawyer JR. The Role of Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis of Pediatric Thoracolumbar Compression Fractures. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2019;39(7):520–523. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001316. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

