Outcomes at 3 years posttransplant in imlifidase-desensitized kidney transplant patients
- PMID: 34236770
- PMCID: PMC9290474
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16754
Outcomes at 3 years posttransplant in imlifidase-desensitized kidney transplant patients
Abstract
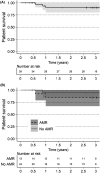
Imlifidase is a cysteine proteinase which specifically cleaves IgG, inhibiting Fc-mediated effector function within hours of administration. Imlifidase converts a positive crossmatch to a potential donor (T cell, B cell, or both), to negative, enabling transplantation to occur between previously HLA incompatible donor-recipient pairs. To date, 39 crossmatch positive patients received imlifidase prior to a kidney transplant in four single-arm, open-label, phase 2 studies. At 3 years, for patients who were AMR+ compared to AMR-, death-censored allograft survival was 93% vs 77%, patient survival was 85% vs 94%, and mean eGFR was 49 ml/min/1.73 m2 vs 61 ml/min/1.73 m2 , respectively. The incidence of AMR was 38% with most episodes occurring within the first month post-transplantation. Sub-analysis of patients deemed highly sensitized with cPRA ≥ 99.9%, and unlikely to be transplanted who received crossmatch-positive, deceased donor transplants had similar rates of patient survival, graft survival, and eGFR but a higher rate of AMR. These data demonstrate that outcomes and safety up to 3 years in recipients of imlifidase-enabled allografts is comparable to outcomes in other highly sensitized patients undergoing HLA-incompatible transplantation. Thus, imlifidase is a potent option to facilitate transplantation among patients who have a significant immunologic barrier to successful kidney transplantation. Clinical Trial: ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02790437), EudraCT Number: 2016-002064-13.
Keywords: alloantibody; clinical research/practice; crossmatch; desensitization; immunosuppressant - other; immunosuppression/immune modulation; kidney transplantation/nephrology; sensitization.
© 2021 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures






Comment in
-
Apples, oranges, and anything in between: In search of the best desensitization therapy.Am J Transplant. 2021 Dec;21(12):3825-3826. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16808. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34416097 No abstract available.
References
-
- Habal MV, Farr M, Restaino S, Chong A. Desensitization in the era of precision medicine: moving from the bench to bedside. Transplantation. 2019;103(8):1574‐1581. - PubMed
-
- Schinstock CA, Smith BH, Montgomery RA, et al. Managing highly sensitized renal transplant candidates in the era of kidney paired donation and the new kidney allocation system: is there still a role for desensitization? Clin Transplant. 2019;33(12):e13751. - PubMed
-
- Vo AA, Petrozzino J, Yeung K, et al. Efficacy, outcomes, and cost‐effectiveness of desensitization using IVIG and rituximab. Transplantation. 2013;95(6):852‐858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

