Atrial Septal Aneurysm and Atrial Septal Defect Association - an Uncommon But Well- Recognized Association
- PMID: 34236809
- PMCID: PMC8522310
- DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0464
Atrial Septal Aneurysm and Atrial Septal Defect Association - an Uncommon But Well- Recognized Association
Abstract
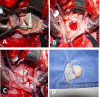
Atrial septal aneurysm (ASA) is an uncommon but wellrecognized cardiac abnormality. This educational text reviews the case of a 54-year-old female presenting an ASA related to a small ostium secundum atrial septal defect. The considerable signs and symptoms, interestingly, have not been justified by the clinical and hemodynamic investigations. So, we opted for a better imaging investigation with cardiac catheterization and transesophageal echocardiography. The surgical process was earlier indicated and performed with aid of cardiopulmonary bypass.
Keywords: Atrial; Cardiopulmonary Bypass; Heart Aneurysm; Heart Septal Defects; Hemodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ruiz de Larrea C, Lasarte JR, Cuadrado A, Pastor E, Galdeano JM, Cabrera A. [Aneurysm of the atrial septum associated with interatrial communication: a study of 12 cases by 2-dimensional color echocardiography] Rev Esp Cardiol. 1993;46(6):340–343. Spanish. - PubMed
-
- Silver MD, Dorsey JS. Aneurysms of the septum primum in adults. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978;102(2):62–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
