Molecular topography of an entire nervous system
- PMID: 34237253
- PMCID: PMC8710130
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.023
Molecular topography of an entire nervous system
Abstract
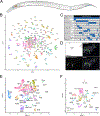
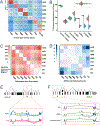
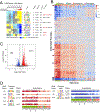
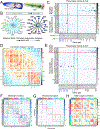
We have produced gene expression profiles of all 302 neurons of the C. elegans nervous system that match the single-cell resolution of its anatomy and wiring diagram. Our results suggest that individual neuron classes can be solely identified by combinatorial expression of specific gene families. For example, each neuron class expresses distinct codes of ∼23 neuropeptide genes and ∼36 neuropeptide receptors, delineating a complex and expansive "wireless" signaling network. To demonstrate the utility of this comprehensive gene expression catalog, we used computational approaches to (1) identify cis-regulatory elements for neuron-specific gene expression and (2) reveal adhesion proteins with potential roles in process placement and synaptic specificity. Our expression data are available at https://cengen.org and can be interrogated at the web application CengenApp. We expect that this neuron-specific directory of gene expression will spur investigations of underlying mechanisms that define anatomy, connectivity, and function throughout the C. elegans nervous system.
Keywords: C. elegans; RNA-seq; cell adhesion molecules; connectome; gene regulatory motifs; neuron; neuropeptides; single-cell.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- 10X Genomics (2017). Application Note - Transcriptional Profiling of 1.3 Million Brain Cells with the Chromium Single Cell 3’ Solution.
-
- Adorjan I, Tyler T, Bhaduri A, Demharter S, Finszter CK, Bako M, Sebok OM, Nowakowski TJ, Khodosevich K, Møllgård K, et al. (2019). Neuroserpin expression during human brain development and in adult brain revealed by immunohistochemistry and single cell RNA sequencing. J. Anat. 235, 543–554. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albertson DG, and Thomson JN (1976). The pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 275, 299–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007149/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G20 RR030956/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS100547/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110391/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

