High-dose irradiation in combination with non-ablative low-dose radiation to treat metastatic disease after progression on immunotherapy: Results of a phase II trial
- PMID: 34237343
- PMCID: PMC11905861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.06.037
High-dose irradiation in combination with non-ablative low-dose radiation to treat metastatic disease after progression on immunotherapy: Results of a phase II trial
Abstract
Aim: To report early findings from a phase II trial of high-dose radiotherapy (HD-RT) with or without low-dose RT (LD-RT) for metastatic cancer.
Methods: Eligible patients had metastatic disease that progressed on immunotherapy within 6 months. Patients were given either HD-RT (20-70 Gy total; 3-12.5 Gy/f), or HD-RT + LD-RT (0.5-2 Gy/f up to 1-10 Gy total) to separate lesions, with continued immunotherapy. Radiographic response was assessed per RECIST 1.1 and Immune-Related Response Criteria (irRC). Primary endpoints: (1) 4-month disease control (DCR, complete/partial response [CR/PR] or stable disease [SD]) or an overall response (ORR, CR/PR) at any point in ≥10% of patients, per RECIST 1.1; (2) dose-limiting toxicity within 3 months not exceeding 30%. Secondary endpoint was lesion-specific response.
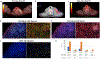
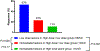
Results: Seventy-four patients (NSCLC, n = 38; melanoma n = 21) were analyzed (39 HD-RT and 35 HD-RT + LD-RT). The median follow-up time was 13.6 months. The primary endpoint was met for 72 evaluable patients, with a 4-month DCR of 42% (47% [16/34] vs. 37% [14/38] in HD-RT + LD-RT vs. HD-RT, P = 0.38), and 19% ORR at any time (26% [9/34] vs. 13% [5/38] in HD-RT + LD-RT vs. HD-RT, P = 0.27). Three patients had toxicity ≥grade 3. LD-RT lesion response (53%) was improved compared to nonirradiated lesions in HD-RT + LD-RT (23%, P = 0.002) and HD-RT (11%, P < 0.001). T- and NK cell infiltration was enhanced in lesions treated with LD-RT.
Conclusions: HD-RT plus LD-RT safely improved lesion-specific response in patients with immune resistant solid tumors by promoting infiltration of effector immune cells into the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: Immunotherapy resistance; Low-dose radiotherapy; Metastatic cancer; Radioimmunotherapy; Salvage radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
JWW declares grants and honoraria from Varian Medical Systems. Outside of the submitted work: JYC declares grants from BMS, personal fees from Varian, Astrazeneca, and Legion, and other from Global Oncology One. SGC declares personal fees from Astrazeneca. SG declares grants from BMS, Astrazeneca, and Nanobiotix; personal fees and other from Novocure. MAD declares grants from Astrazeneca and Genentech, personal fees from BMS, Apexigen, Novartis, and Array. DSH declares grants from AbbVie, Aldi-Norte, Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Fate Therapuetics, Genmab, GSK, Ignyta, Kite, Kyowa, Eli Lilly, LOXO, Merk, MedImmune Mirati, miRNA, Molecular Templates, Mologen, NCI-CTEP, Novartis, Seattle Genetics, Turning Point Therapeutics; personal fees from Alpha Insights, Axiom, Baxter, eCancer, GLG, Group H, Guidepoint, Liberium, Medscape, Numab, Oncology Education Project Association, Prime Oncology, Trieza Therapuetics, WebMD; grants and personal fees from Adaptimmune, Amgen, Bayer, Genentech, Infinity, Pfizer, Takeda. Non-financial support from AACR, ASCO, POET, CCLO, SITC; advisor for Molecular Match, OncoResponse, Presagia Inc. JVH declares grants and other from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Spectrum; other from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Catalyst, EMD Serono, Foundation Medicine, Hengrui Therapeutics, Genentech/Roche, Guardant Health, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Takeda. MEC declares grants from Genetech and Merck. JWW reports grants from Bristol-Meyers Squibb; personal fees and other from Alpine Immune Sciences, Legion Healthcare Partners, Molecular Match, Nanorobotix, OncoResponse, and RefleXion Medical; grants and personal fees from Nanobiotics; grants, personal fees, and other from Checkmate Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
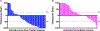
Similar articles
-
Fostering efficacy of anti-PD-1-treatment: Nivolumab plus radiotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer - study protocol of the FORCE trial.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):1074. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6205-0. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31703637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pembrolizumab with or without radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 May;9(5):467-475. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30391-X. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33096027 Clinical Trial.
-
Pembrolizumab with or without radiation therapy for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized phase I/II trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Oct;8(2):e001001. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001001. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33051340 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: preclinical and early clinical data.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004 Feb;18(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(03)00138-2. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15005280 Review.
-
Efficacy of adoptive therapy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and recombinant interleukin-2 in advanced cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;30(12):1902-1913. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz398. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31566658
Cited by
-
A 'Hybrid' Radiotherapy Regimen Designed for Immunomodulation: Combining High-Dose Radiotherapy with Low-Dose Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 19;14(14):3505. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143505. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-dose irradiation for reversing immunotherapy resistance: how to translate?J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jul;10(7):e004939. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004939. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35835490 Free PMC article.
-
Application of individualized multimodal radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy in metastatic tumors.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1106644. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1106644. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined treatment of non-small cell lung cancer using radiotherapy and immunotherapy: challenges and updates.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Nov;41(11):1086-1099. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12226. Epub 2021 Oct 17. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34658186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Use of Low-Dose Radiotherapy to Modulate the Tumor Microenvironment of Liver Metastases.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 15;12:812210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.812210. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2342–50. - PubMed
-
- Hui R, Özgüroğlu M, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, et al. Patient-reported outcomes with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III, unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer (PACIFIC): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1670–80. - PubMed
-
- Kwon ED, Drake CG, Scher HI, Fizazi K, Bossi A, van den Eertwegh AJ, et al. Ipilimumab versus placebo after radiotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that had progressed after docetaxel chemotherapy (CA184–043): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:700–12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

