NT157 Inhibits HCC Migration via Downregulating the STAT3/Jab1 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34238066
- PMCID: PMC8274079
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211027916
NT157 Inhibits HCC Migration via Downregulating the STAT3/Jab1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: The high fatality-to-case ratio of hepatocellular carcinoma is directly related to metastasis. The signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 is a key mediator of the cytokine and growth factor signaling pathways and drives the transcription of genes responsible for cancer-associated phenotypes. However, so far, no specific inhibitor for signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 has been used in clinical practice. Therefore, targeting the signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 for cancer therapy is highly desired to improve outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Experimental design: Using the small-molecule inhibitor NT157, the effect of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 inhibition on cell migration was tested in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and a lung metastasis model of the disease.
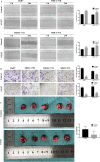
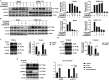
Results: NT157 significantly inhibited the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro and lung metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo. Mechanistically, it inhibited the phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, NT157 treatment suppressed the c-Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 levels in the nucleus but no significant decrease was observed in its expression in the cytoplasm. Finally, high mRNA expression levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and c-Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma were associated with significantly low survival rates.
Conclusion: NT157 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma migration and metastasis by downregulating the signal transducer and activator of transcription-3/c-Jun activation domain-binding protein-1 signaling pathway and targeting it may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy for the clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma in the future.
Keywords: Jab1; NT157; STAT3; hepatocellular carcinoma; metastasis; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394-424. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Villanueva A, Lachenmayer A, Finn RS. Advances in targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma in the genomic era. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(7):408-424. - PubMed
-
- Ryu SH, Jang MK, Kim WJ, Lee D, Chung YH. Metastatic tumor antigen in hepatocellular carcinoma: golden roads toward personalized medicine. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33(4):965-980. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, et al. STAT3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999;98(3):295-303. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE, Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277(5332):1630-1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

