Diagnostic yield of routine daily blood culture in patients on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 34238367
- PMCID: PMC8264470
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03658-7
Diagnostic yield of routine daily blood culture in patients on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are frequent on veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-A ECMO). Performing routine blood cultures (BCs) may identify early paucisymptomatic BSIs. We investigated the contribution of systematic daily BCs to detect BSIs on V-A ECMO.
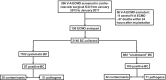
Methods: This was a retrospective study including all adult patients requiring V-A ECMO and surviving more than 24 h. Our protocol included routine daily BCs, from V-A ECMO insertion up to 5 days after withdrawal; other BCs were performed on-demand.
Results: On the 150 V-A ECMO included, 2146 BCs were performed (1162 routine and 984 on-demand BCs); 190 (9%) were positive, including 68 contaminants. Fifty-one (4%) routine BCs revealed BSIs; meanwhile, 71 (7%) on-demand BCs revealed BSIs (p = 0.005). Performing routine BCs was negatively associated with BSIs diagnosis (OR 0.55, 95% CI [0.38; 0.81], p = 0.002). However, 16 (31%) BSIs diagnosed by routine BCs would have been missed by on-demand BCs. Independent variables for BSIs diagnosis after routine BCs were: V-A ECMO for cardiac graft failure (OR 2.43, 95% CI [1.20; 4.92], p = 0.013) and sampling with on-going antimicrobial therapy (OR 2.15, 95% CI [1.08; 4.27], p = 0.029) or renal replacement therapy (OR 2.05, 95% CI [1.10; 3.81], p = 0.008). Without these three conditions, only two BSIs diagnosed with routine BCs would have been missed by on-demand BCs sampling.
Conclusions: Although routine daily BCs are less effective than on-demand BCs and expose to contamination and inappropriate antimicrobial therapy, a policy restricted to on-demand BCs would omit a significant proportion of BSIs. This argues for a tailored approach to routine daily BCs on V-A ECMO, based on risk factors for positivity.
Keywords: Blood culture; Bloodstream infection; Cardiogenic shock; Contamination; Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
NM serves as a consultant for Amomed. The other authors have not disclosed any potential competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical