Anti-C5 Antibody Tesidolumab Reduces Early Antibody-mediated Rejection and Prolongs Survival in Renal Xenotransplantation
- PMID: 34238812
- PMCID: PMC8915445
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004996
Anti-C5 Antibody Tesidolumab Reduces Early Antibody-mediated Rejection and Prolongs Survival in Renal Xenotransplantation
Abstract
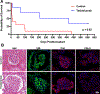
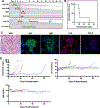
Objective: Pig-to-primate renal xenotransplantation is plagued by early antibody-mediated graft loss which precludes clinical application of renal xenotransplantation. We evaluated whether temporary complement inhibition with anti-C5 antibody Tesidolumab could minimize the impact of early antibody-mediated rejection in rhesus monkeys receiving pig kidneys receiving costimulatory blockade-based immunosuppression.
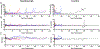
Methods: Double (Gal and Sda) and triple xenoantigen (Gal, Sda, and SLA I) pigs were created using CRISPR/Cas. Kidneys from DKO and TKO pigs were transplanted into rhesus monkeys that had the least reactive crossmatches. Recipients received anti-C5 antibody weekly for 70 days, and T cell depletion, anti-CD154, mycophenolic acid, and steroids as baseline immunosuppression (n = 7). Control recipients did not receive anti-C5 therapy (n = 10).
Results: Temporary anti-C5 therapy reduced early graft loss secondary to antibody-mediated rejection and improved graft survival (P < 0.01). Deleting class I MHC (SLA I) in donor pigs did not ameliorate early antibody-mediated rejection (table). Anti-C5 therapy did not allow for the use of tacrolimus instead of anti-CD154 (table), prolonging survival to a maximum of 62 days.
Conclusion: Inhibition of the C5 complement subunit prolongs renal xenotransplant survival in a pig to non-human primate model.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
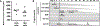
References
-
- Dorling A. Are anti-endothelial cell antibodies a pre-requisite for the acute vascular rejection of xenografts? Xenotransplantation. 2003;10(1):16–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

