A SNAI2-PEAK1-INHBA stromal axis drives progression and lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by supporting subpopulations of tumor cells positive for antiapoptotic and stress signaling markers
- PMID: 34239043
- PMCID: PMC8376636
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-01906-2
A SNAI2-PEAK1-INHBA stromal axis drives progression and lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer by supporting subpopulations of tumor cells positive for antiapoptotic and stress signaling markers
Abstract
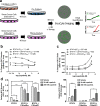
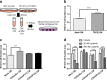
Intercellular mechanisms by which the stromal microenvironment contributes to solid tumor progression and targeted therapy resistance remain poorly understood, presenting significant clinical hurdles. PEAK1 (Pseudopodium-Enriched Atypical Kinase One) is an actin cytoskeleton- and focal adhesion-associated pseudokinase that promotes cell state plasticity and cancer metastasis by mediating growth factor-integrin signaling crosstalk. Here, we determined that stromal PEAK1 expression predicts poor outcomes in HER2-positive breast cancers high in SNAI2 expression and enriched for MSC content. Specifically, we identified that the fibroblastic stroma in HER2-positive breast cancer patient tissue stains positive for both nuclear SNAI2 and cytoplasmic PEAK1. Furthermore, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) express high PEAK1 protein levels and potentiate tumorigenesis, lapatinib resistance and metastasis of HER2-positive breast cancer cells in a PEAK1-dependent manner. Analysis of PEAK1-dependent secreted factors from MSCs revealed INHBA/activin-A as a necessary factor in the conditioned media of PEAK1-expressing MSCs that promotes lapatinib resistance. Single-cell CycIF analysis of MSC-breast cancer cell co-cultures identified enrichment of p-Akthigh/p-gH2AXlow, MCL1high/p-gH2AXlow and GRP78high/VIMhigh breast cancer cell subpopulations by the presence of PEAK1-expressing MSCs and lapatinib treatment. Bioinformatic analyses on a PEAK1-centric stroma-tumor cell gene set and follow-up immunostaining of co-cultures predict targeting antiapoptotic and stress pathways as a means to improve targeted therapy responses and patient outcomes in HER2-positive breast cancer and other stroma-rich malignancies. These data provide the first evidence that PEAK1 promotes tumorigenic phenotypes through a previously unrecognized SNAI2-PEAK1-INHBA stromal cell axis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Yuan S, Norgard RJ, Stanger BZ. Cellular plasticity in cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:837–851. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marusyk A, Tabassum DP, Janiszewska M, Place AE, Trinh A, Rozhok AI, et al. Spatial proximity to fibroblasts impacts molecular features and therapeutic sensitivity of breast cancer cells influencing clinical outcomes. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6495–6506. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1457. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

