Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: a guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices
- PMID: 34239102
- PMCID: PMC8592384
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01197-1
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: a guide for annotation, quantification and best reporting practices
Abstract
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approaches can enable detection and quantification of many thousands of metabolite features simultaneously. However, compound identification and reliable quantification are greatly complicated owing to the chemical complexity and dynamic range of the metabolome. Simultaneous quantification of many metabolites within complex mixtures can additionally be complicated by ion suppression, fragmentation and the presence of isomers. Here we present guidelines covering sample preparation, replication and randomization, quantification, recovery and recombination, ion suppression and peak misidentification, as a means to enable high-quality reporting of liquid chromatography- and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics-derived data.
Figures
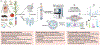

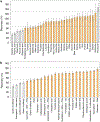

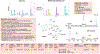
References
-
- Doerr A Global metabolomics. Nat. Methods 14, 32 (2017).
-
- Fessenden M Metabolomics: small molecules, single cells. Nature 540, 153–155 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Oliver SG, Winson MK, Kell DB & Baganz F Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 16, 373–378 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Alseekh S & Fernie AR Metabolomics 20 years on: what have we learned and what hurdles remain? Plant J. 94, 933–942 (2018). - PubMed
-
-
Chevalier C et al. Gut microbiota orchestrates energy homeostasis during cold. Cell 163, 1360–1374 (2015).
This paper demonstrates that the microbiota is a key factor orchestrating overall energy homeostasis during increased demand in mammals.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

